Users often attribute low storage to third-party applications or an increasing number of personal files. However, Windows itself can silently consume a substantial amount of disk space. If a system drive consistently fills up unexpectedly, native Windows features are frequently the underlying reason. This guide explains how to recover gigabytes of storage in just a few minutes.
System Restore
System Restore is a valuable tool for resolving Windows issues, allowing a system rollback to an earlier state. Windows automatically generates restore points before significant events like updates or driver installations. These points accumulate until the designated storage limit is reached, at which point older points are removed to accommodate new ones.
To manage the space consumed by this feature, users can configure Windows to retain only a few restore points. Search for ‘Create a restore point’ and select the relevant option. Within the System Properties window, navigate to the ‘System Protection’ tab, choose the system drive, and click ‘Configure’.
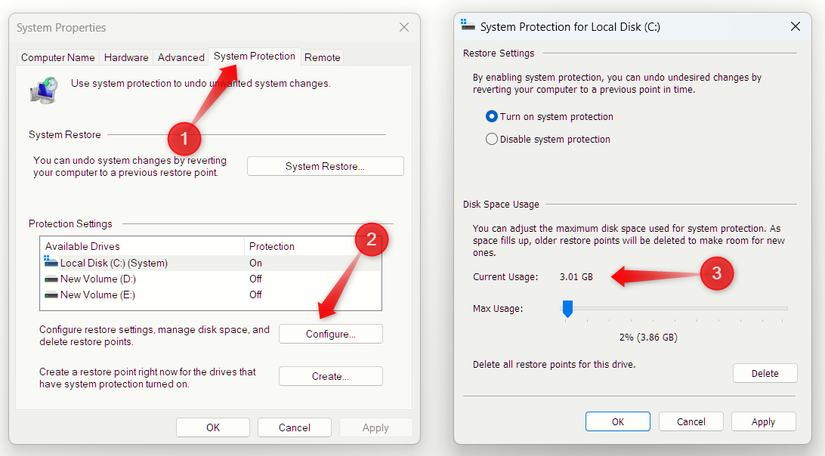
The ‘Current Usage’ display shows the space presently occupied by System Restore. The ‘Max Usage’ slider allows adjustment of the maximum disk space Windows dedicates to this feature.
Reserved Storage
Windows allocates a portion of the drive as Reserved Storage. This ensures adequate space for updates, applications, and temporary files, which helps maintain proper system operation and prevents update issues. This feature typically uses 7–10 GB by default and may expand over time. Disabling this reserved space is generally not recommended, as it contributes to smooth updates and system performance.
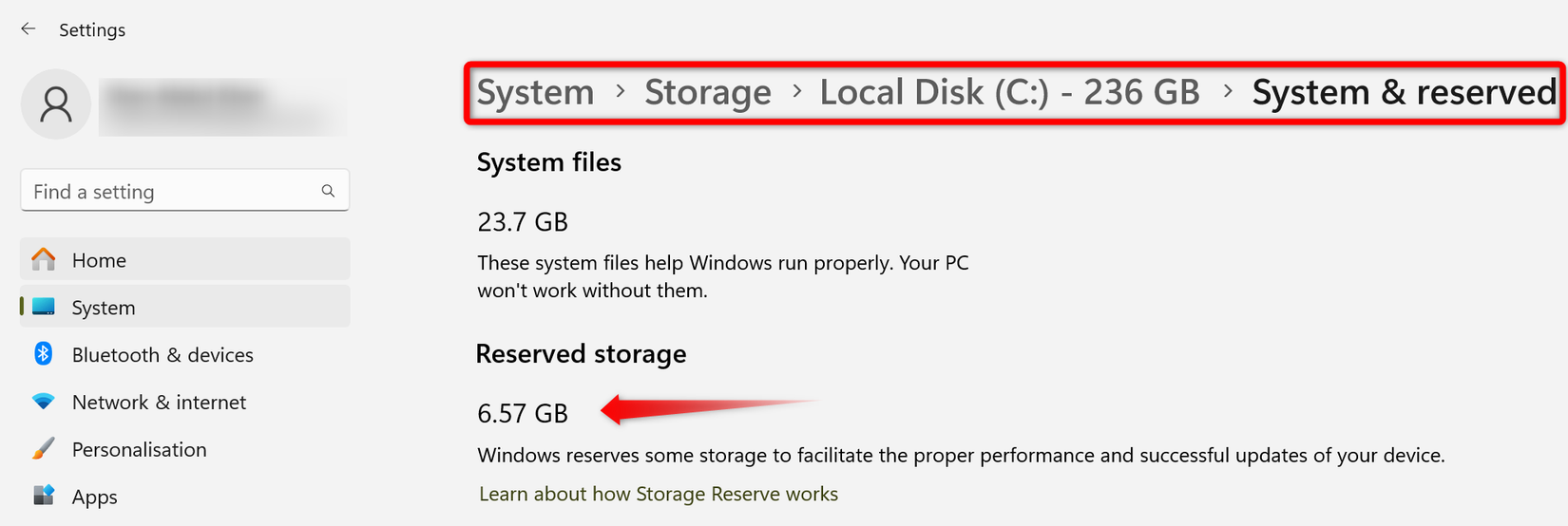
Nevertheless, in situations of critically low storage, this space can be temporarily reclaimed. To ascertain the amount of space utilized by Reserved Storage, navigate to Settings > System > Storage, then click ‘Show More Categories’ > ‘System & Reserved’.
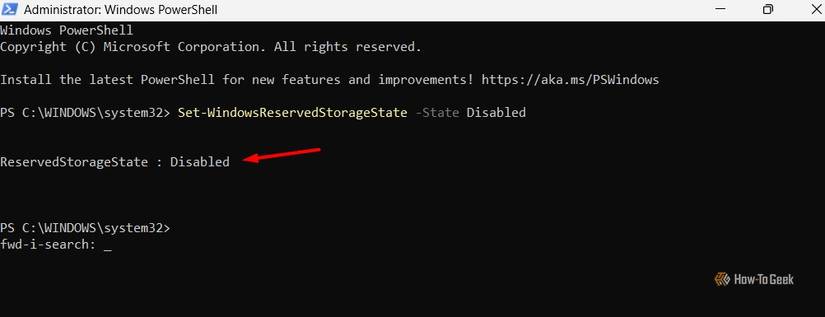
Windows does not offer a direct setting to disable this feature; therefore, PowerShell is required. Search for ‘PowerShell’ in Windows Search, right-click the application, and choose ‘Run as Administrator’. Execute the following command to release the reserved storage:
Set-WindowsReservedStorageState -State Disabled
Hibernation File (hiberfil.sys)
Consider the last time the PC’s hibernate feature was utilized. If the answer is ‘never’ or ‘not recently,’ several gigabytes of storage, often equivalent to the installed RAM, might be going unused. Hibernation saves open applications and documents, allowing a seamless return to the previous work state. If this feature is not used, its allocated disk space can be recovered.
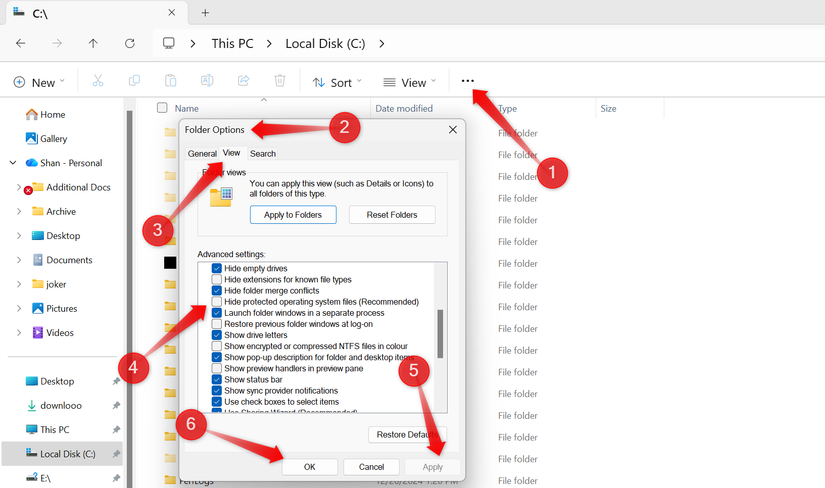
To determine the space consumed by this feature, the ‘hiberfil.sys’ file must first be made visible. Navigate to the ‘View’ tab, then click ‘Show’ > ‘Hidden Items’.
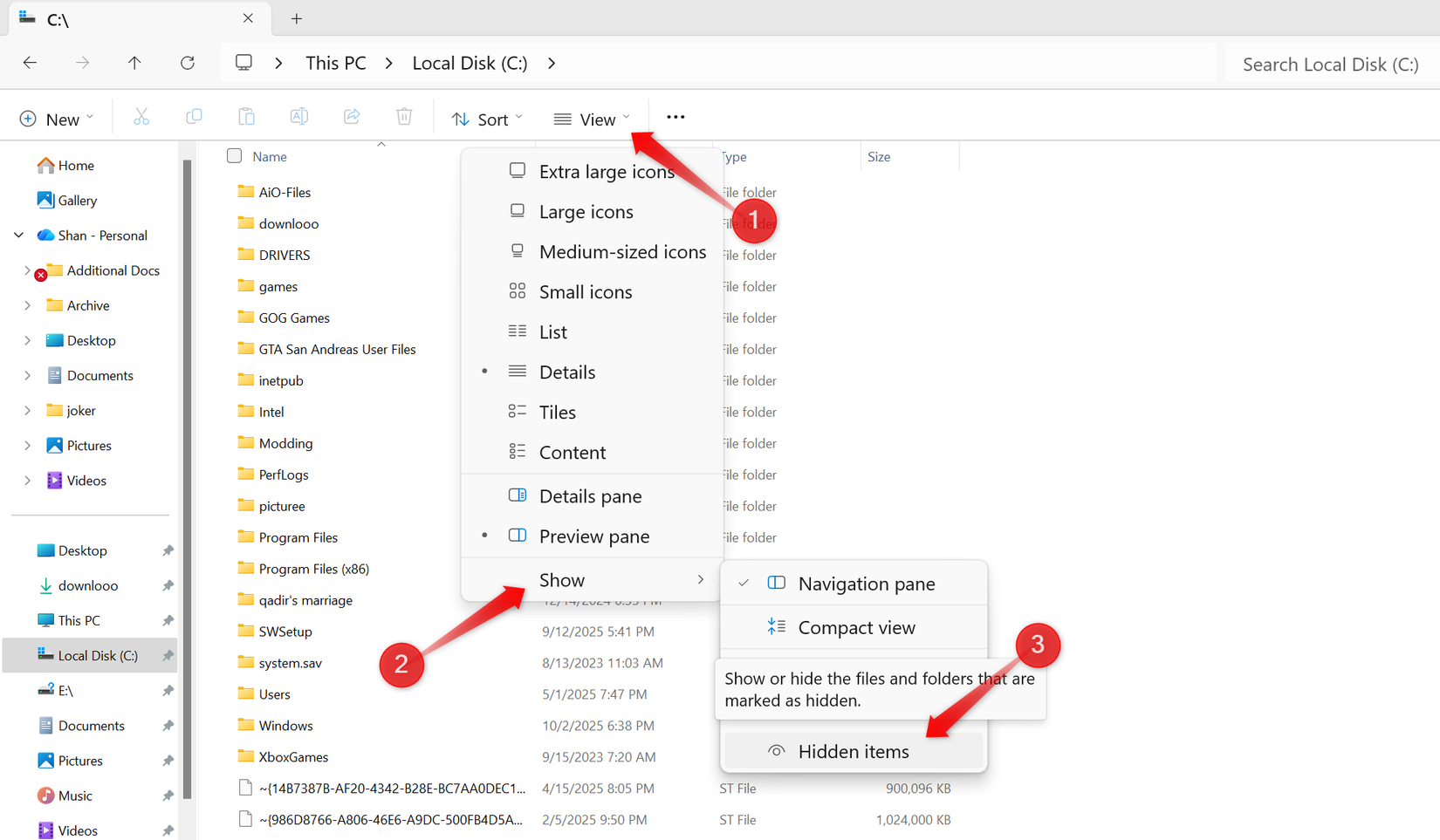
Next, click the three horizontal dots, select ‘Options’, proceed to the ‘View’ tab, and uncheck ‘Hide protected operating system files (Recommended)’. Confirm by clicking ‘Apply’ and then ‘OK’.
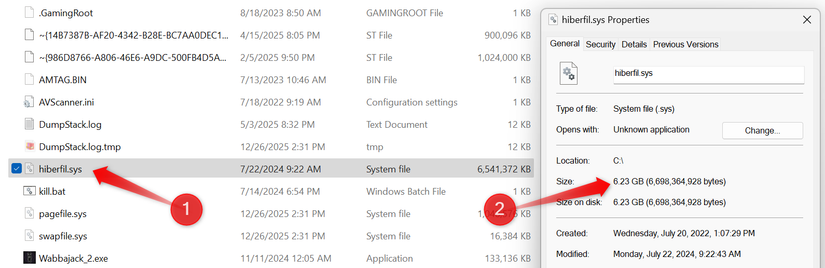
Subsequently, right-click the ‘hiberfil.sys’ file, select ‘Properties’, and the occupied storage in gigabytes will be displayed.
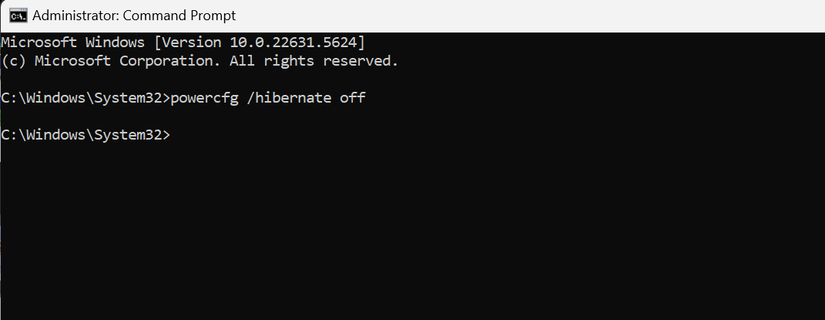
To disable hibernation and remove the ‘hiberfil.sys’ file, use Command Prompt. Search for ‘Command Prompt’, right-click it, and select ‘Run as Administrator’. Then enter:
powercfg /hibernate off
Press Enter, restart the computer, and the hiberfil.sys file will be removed, freeing up valuable storage space.
Feature update rollback files (Windows.old)
Windows maintains a backup of the previous system state, enabling a rollback in case of a problematic update. This backup resides in the ‘Windows.old’ folder, containing older system files, drivers, and settings, frequently occupying 10–30 GB or more. If the current update is stable and a rollback is not anticipated, deleting this folder can release substantial disk space.
While Windows typically removes the Windows.old folder automatically after approximately 10 days, it can be deleted sooner if storage is limited. To do this, right-click the Start button, open ‘Settings’, navigate to System > Storage, click ‘Temporary Files’, check the box next to ‘Temporary Windows Installation Files’, and then click ‘Remove Files’.
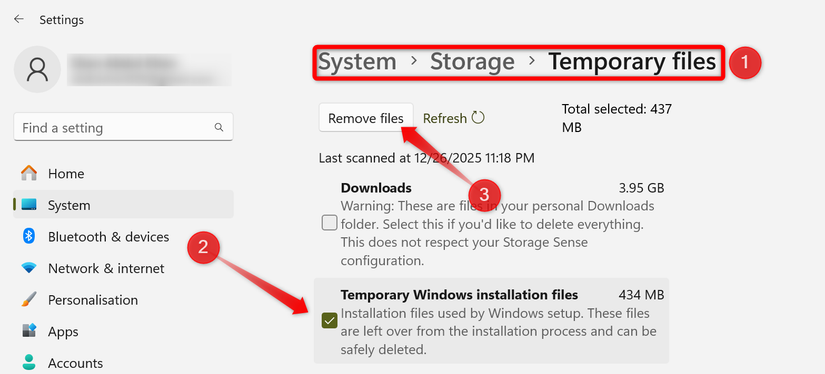
Note that deleting this folder only eliminates the integrated rollback capability. A manual installation can still be used for future rollbacks if necessary.
Hyper-V virtualization
If Hyper-V has been used to create virtual machines, test Linux, or explore development tools, this section is relevant. However, if it was used once and then abandoned, residual virtual hard disks, snapshots, and configuration files might be consuming 10–50 GB, or even more with multiple VMs or snapshots.
Furthermore, simply removing a VM from Hyper-V Manager does not always eliminate all associated files. Ensure that any unused VMs are properly deleted from Hyper-V Manager, and then manually inspect the default VM storage folders for any remaining ‘.vhdx’ files. After cleanup, disable Hyper-V and other virtualization features via Windows Features to avoid unnecessary storage consumption.
Storage depletion is not exclusively due to excessive application installations or accumulated files. Windows often silently uses significant disk space for features that many users overlook. Fortunately, this storage usage is neither concealed nor permanent. The provided suggestions can help identify space-consuming elements, determine actual needs, and recover several gigabytes.