
Introducing Gradio
Gradio is a Python framework designed to simplify the creation of interactive web interfaces for machine learning models. It allows users to build sophisticated applications with minimal code, supporting diverse inputs like text, images, and audio, and presenting outputs clearly. Gradio aims to make model deployment accessible to researchers, data scientists, and developers alike.
Key benefits of using Gradio include:
- Rapid conversion from model to interactive demo.
- No frontend development skills required, relying solely on Python.
- Extensive support for various data types, including text, images, and audio.
- Simple local deployment and free public hosting options.
Installing Gradio and Basic Setup
To begin using Gradio, install the package via pip:
pip install gradioWith Gradio installed, the next step is to create a basic application. Create a file named gradio_app.py and insert the following code:
import gradio as gr
def greet(name):
return f"Hello {name}!"
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=greet,
inputs="text",
outputs="text",
title="Greeting App"
)
demo.launch()Executing this script with python gradio_app.py will launch a web application accessible at http://127.0.0.1:7860/. The interface automatically generates a text input field, a submit button, and a text output area based on the provided specifications.
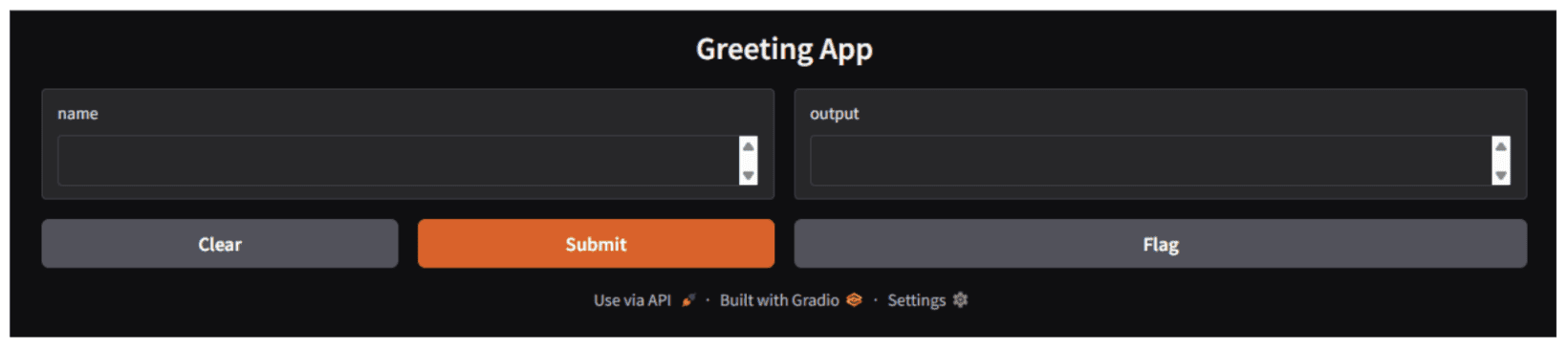
Understanding the Gradio Interface
The gr.Interface class serves as Gradio’s high-level API, simplifying complex interactions. It mandates three core components:
- Function (fn): A Python function designed to process inputs.
- Inputs: Defines the type(s) of input expected.
- Outputs: Specifies the type(s) of output produced.
Exploring Input and Output Components
While basic strings like “text”, “image”, or “audio” can define components, Gradio provides enhanced control through dedicated component classes.
import gradio as gr
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=lambda x: x,
inputs=gr.Textbox(lines=2, placeholder="Enter text here..."),
outputs=gr.Textbox(label="Output")
)Frequently used components include:
- gr.Textbox(): For multi-line text input.
- gr.Image(): For image uploads and previews.
- gr.Audio(): For handling audio files.
- gr.Checkbox(): For boolean inputs.
- gr.Slider(): For numerical range selection.
- gr.Radio(): For multiple-choice selections.
- gr.Dropdown(): For selecting from a list of options.
Handling Multiple Inputs and Outputs
Applications in real-world scenarios frequently involve multiple inputs or generate multiple outputs. Gradio manages these situations effectively using lists.
import gradio as gr
def process_form(name, is_morning, temperature):
greeting = "Good morning" if is_morning else "Hello"
message = f"{greeting}, {name}! Temperature: {temperature}°C"
return message, temperature * 1.8 + 32 # Convert to Fahrenheit
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=process_form,
inputs=[
gr.Textbox(label="Name"),
gr.Checkbox(label="Is it morning?"),
gr.Slider(0, 100, label="Temperature (°C)")
],
outputs=[
gr.Textbox(label="Greeting"),
gr.Number(label="Temperature (°F)")
]
)
demo.launch()Output:
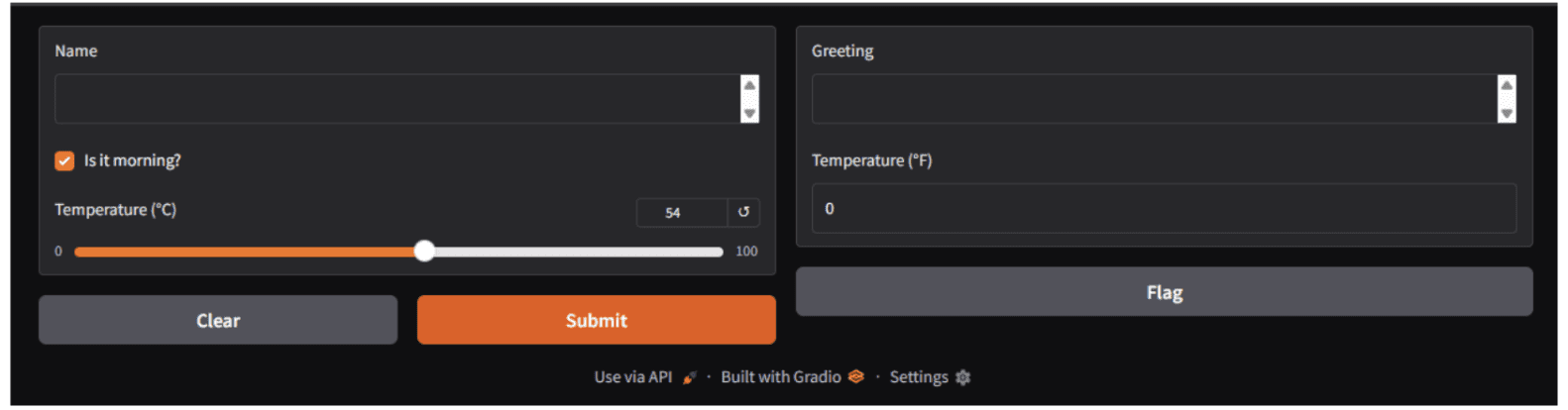
When incorporating multiple inputs, the function must be designed to accept an equivalent number of parameters. Likewise, functions producing multiple outputs should return multiple values.
Processing Images
Gradio simplifies the demonstration of image processing models:
import gradio as gr
import numpy as np
def apply_sepia(image):
# Image comes as numpy array with shape (height, width, channels)
sepia_filter = np.array([[0.393, 0.769, 0.189],
[0.349, 0.686, 0.168],
[0.272, 0.534, 0.131]])
sepia_image = image.dot(sepia_filter.T)
sepia_image = np.clip(sepia_image, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
return sepia_image
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=apply_sepia,
inputs=gr.Image(label="Input Image"),
outputs=gr.Image(label="Sepia Filtered"),
title="Sepia Filter App"
)
demo.launch()Output:

The gr.Image component automates file uploads, previews, and the conversion of images into NumPy arrays for subsequent processing.
Handling Audio Processing
Developing audio applications is equally simple:
import gradio as gr
def transcribe_audio(audio):
return "Transcribed text would appear here"
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=transcribe_audio,
inputs=gr.Audio(label="Upload Audio", type="filepath"),
outputs=gr.Textbox(label="Transcription"),
title="Speech-to-Text Demo"
)
demo.launch()In a practical application, a speech recognition model would typically be invoked within the transcribe_audio(audio) function. For demonstration purposes, a placeholder value is returned.
Output:
Creating Advanced Layouts with Gradio Blocks
While gr.Interface is suitable for straightforward applications, gr.Blocks provides extensive control over layout and data flow. Blocks functions as a low-level API, enabling the construction of complex, multi-step applications.
Implementing a Basic Blocks Example
import gradio as gr
def greet(name):
return f"Hello {name}!"
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
name_input = gr.Textbox(label="Your Name")
greet_button = gr.Button("Greet")
output = gr.Textbox(label="Greeting")
greet_button.click(
fn=greet,
inputs=name_input,
outputs=output
)
demo.launch()Output:

Building Complex Layouts with Rows and Columns
A more advanced example demonstrates integration with Transformers. Ensure the Transformers package is installed on the system.
pip install transformers
import gradio as gr
from transformers import pipeline
# Load a translation model
translator = pipeline("translation_en_to_de", model="t5-small")
def translate_text(text):
result = translator(text, max_length=40)[0]
return result['translation_text']
with gr.Blocks(title="English to German Translator") as demo:
gr.Markdown("# 🌍 English to German Translator")
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
english_input = gr.Textbox(
label="English Text",
placeholder="Enter text to translate...",
lines=4
)
translate_btn = gr.Button("Translate", variant="primary")
with gr.Column():
german_output = gr.Textbox(
label="German Translation",
lines=4
)
# Add example prompts
gr.Examples(
examples=[
["Hello, how are you?"],
["The weather is beautiful today"],
["Machine learning is fascinating"]
],
inputs=english_input
)
translate_btn.click(
fn=translate_text,
inputs=english_input,
outputs=german_output
)
demo.launch()Output:

Managing State in Gradio Applications
Effective state management is crucial for interactive applications. Gradio offers two primary methods: global state and session state.
Managing Session State (User-Specific)
For managing user-specific state, Gradio’s integrated state management features can be utilized. The subsequent example illustrates basic chatbot logic that employs state to preserve conversation history.
import gradio as gr
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(label="Conversation")
msg = gr.Textbox(label="Your Message")
clear = gr.Button("Clear")
state = gr.State([])
def user_message(message, history):
# Update history with user message and placeholder for bot
return "", history + [[message, None]]
def bot_response(history):
# Simple echo bot logic
response = f"I received: {history[-1][0]}"
history[-1][1] = response
return history
msg.submit(
user_message,
[msg, state],
[msg, state]
).then(
bot_response,
state,
chatbot
)
clear.click(lambda: (None, []), None, [chatbot, state])
demo.launch()Deploying and Sharing Your Applications
For rapid sharing, Gradio can generate a public URL:
demo.launch(share=True)This action produces a temporary, publicly accessible link, ideal for demonstrations and quick sharing among collaborators. The link typically remains valid for 72 hours.
For free, permanent hosting, consider these steps:
- Establish a Hugging Face account.
- Initiate a new Space, selecting Gradio as the Software Development Kit (SDK).
- Upload the necessary application files: app.py (the primary application file) and requirements.txt (listing Python dependencies). An example of a requirements.txt file content is provided below:
torch
transformers- Push the code to Git:
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit"
git pushThe application will then be accessible at https://huggingface.co/spaces/your-username/your-space-name.
Gradio applications are deployable on any platform supporting Python web applications, including:
- Utilizing demo.launch(server_name=”0.0.0.0″, server_port=7860).
- Packaging the application and its dependencies within a Docker container.
- Deployment on cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure.
Building an Image Classification Dashboard
To consolidate the learned concepts, an image classification dashboard can be constructed. This project involves a straightforward image classification dashboard developed using PyTorch and Gradio. It facilitates users in uploading an image via a web interface to obtain the top five predicted classes from a pre-trained deep learning model.
The project utilizes ResNet-50, a widely recognized convolutional neural network pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset. As the model is pre-trained, no custom training or labeled data is necessary for this project. Its purpose is for demonstration, experimentation, and educational contexts, not for production deployment.
Gradio is employed to furnish a lightweight user interface, allowing direct model interaction from a web browser.
import gradio as gr
import torch
from torchvision import models, transforms
from PIL import Image
# Load pre-trained model
model = models.resnet50(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
# Preprocessing
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
)
])
def classify_image(image):
image = Image.fromarray(image)
input_tensor = preprocess(image)
input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_batch)
# Get top 5 predictions
probabilities = torch.nn.functional.softmax(output[0], dim=0)
top5_prob, top5_catid = torch.topk(probabilities, 5)
results = []
for i in range(top5_prob.size(0)):
results.append(f"Category {top5_catid[i].item()}: {top5_prob[i].item()*100:.2f}%")
return "\n".join(results)
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=classify_image,
inputs=gr.Image(label="Upload Image"),
outputs=gr.Textbox(label="Top 5 Predictions"),
title="Image Classifier"
)
demo.launch()Wrapping Up
Gradio simplifies machine learning deployment by removing conventional obstacles between model development and user interaction. This crash course covered the essentials of building Gradio interfaces, designing with components for various input/output types, creating advanced layouts with Gradio Blocks, managing state in interactive applications, and implementing deployment strategies for sharing projects.
Gradio’s core strength lies in its simplicity and adaptability. Whether developing a rapid prototype for internal evaluation or a refined application for public access, Gradio offers the necessary tools to operationalize machine learning models.


