The global real-time payments market is experiencing substantial growth. Fortune Business Insights reported the market value at USD 24.91 billion in 2024, with projections to reach USD 284.49 billion by 2032, showing a CAGR of 35.4%. Concurrently, Grand View Research indicated the global mobile payment market, valued at USD 88.50 billion in 2024, is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 38.0% from 2025 to 2030. (Note: Third-party market research and statistics are for informational purposes only. AWS and IBM do not guarantee the accuracy of this information.)
This rapid expansion highlights the critical need for financial institutions to modernize their payment processing infrastructure. Institutions must handle high transaction volumes with minimal latency to meet strict service level agreements (SLAs) and support the increasing demand for mobile payments.
However, conventional payment orchestration systems, frequently based on monolithic architectures, often struggle with these requirements, facing issues related to latency, availability, and scalability. Furthermore, dependence on on-premises infrastructure results in elevated costs and hinders innovation, emphasizing the necessity for modernization.
With sustainability gaining importance, organizations are adopting cloud-based solutions to optimize infrastructure, decrease carbon footprints, and improve energy efficiency. This transition offers scalability and performance, aligning with global sustainability objectives and ensuring the future of real-time payments.
This article explores a real-time payment orchestration framework. It employs an event-driven architecture and AWS serverless services to boost the resilience, efficiency, and scalability of real-time payments. By breaking down payment processing into distinct business capabilities, financial institutions can achieve greater modularity and flexibility. Tenant-based segregation supports data isolation and security. Moreover, utilizing asynchronous communication via Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) improves both scalability and resilience.
Traditional Real-Time Payment Orchestration
Payment orchestration functions as a middleware solution, simplifying transaction processing across various payment methods, gateways, and financial institutions. It manages essential business functions like payment authorization, processing, settlement and clearing, compliance and risk management, and account management for both incoming and outgoing payment flows.
The diagram below illustrates the high-level business capabilities that payment orchestrators support across different payment flows, such as real-time payments, digital disbursements, tax payments, and wire transfers.

Detailed flowchart depicting a payment processing system with multiple components. The diagram shows primary payment types at the top (including Realtime Payments, Digital Disbursement, Credit Transfer, and Peer to Peer Payments) flowing down through core processing stages including Payment Acceptance, Execution, Clearing, Reporting, Tracking, Reversals, and Billing.
Many financial institutions utilize a tenant-based approach, often structured by geography, because of diverse clearing processes, local regulations, and transaction requirements across AWS Regions. Without adequate service separation, however, teams may incorporate region-specific logic into existing services, leading to increased monolithic complexity and shared infrastructure for all payment flows.
Conventional payment systems process transactions sequentially, where each step must finish before the next can begin. Yet, an examination of payment workflows uncovers several opportunities for parallel execution:
- Sanctions screening and fraud detection – Compliance and fraud checks can occur concurrently with initial routing decisions, instead of sequentially blocking subsequent processing.
- Payment routing and authorization requests – Once basic validations are complete, routing and authorization can proceed in parallel rather than sequentially.
- Payment execution and ledger updates – The actual payment execution does not need to await ledger record updates; these processes can happen concurrently.
- Settlement, reconciliation, and tracking – These post-transaction processes can be initiated independently once the primary transaction is complete.
This parallel methodology can significantly enhance throughput and decrease latency compared to conventional queue-based systems, where operations form a sequential chain, prolonging processing time and creating bottlenecks.
Most legacy payment orchestration systems heavily depend on on-premises virtual machines (VMs), which presents several challenges:
- Multi-Region support for disaster recovery and multi-tenancy leads to substantial capital expenditure and operational overhead.
- High latency and SLA issues arise from sequential message processing and delays between geographically separated data centers.
- Payment flow reusability is limited because monolithic architectures necessitate region-specific adjustments for local clearing mechanisms and regulations, increasing complexity and costs.
- Scalability challenges and high memory consumption result from inefficient resource utilization and the execution of irrelevant logic across regions.
- Complex cross-border payment routing is caused by variations in clearing rules, transaction limits, and local regulations, leading to increased latency and routing errors.
- Integration challenges with diverse data formats occur because legacy systems depend on proprietary standards (e.g., ISO 20022, SWIFT MT), complicating data conversion and compliance.
- Deployment of new payment flows is highly complex due to monolithic architectures requiring extensive region-specific modifications, which slows time to market.
- On-premises infrastructure contributes to environmental impact and a high carbon footprint by consuming excessive energy, while cloud-based approaches enhance efficiency.
Solution Overview
To address these challenges, the proposed architecture incorporates the following design principles for developing a future-ready, real-time payment orchestration solution:
- Performance at scale – The solution aims to handle over 1,000 transactions per second (TPS) with consistent low latency under diverse load conditions.
- High availability – The goal is to achieve 99.999% uptime, satisfying the stringent requirements of financial transactions.
- Geographic resilience – The architecture supports global operations with region-specific compliance while sustaining consistent performance.
- Cost optimization – Total cost of ownership is reduced through efficient resource utilization and serverless technologies.
- Security and compliance – The solution supports data protection and regulatory adherence across various jurisdictions.
- Operational simplicity – Deployment, monitoring, and maintenance are streamlined across the payment ecosystem.
- Microservices – Payment processing is decomposed into distinct business capabilities, allowing financial institutions to enhance modularity and flexibility. This microservices approach enables independent scaling and development of critical components.
The diagram below illustrates the high-level solution architecture for real-time payments. Existing channels using synchronous or asynchronous APIs can be adapted to use edge-optimized endpoints, which helps reduce latency.

Architecture diagram detailing an AWS-based payment orchestration platform utilizing event-driven principles. Features reusable components across two regions, with dedicated modules for payment initiation, execution, reconciliation, billing, and risk management. Implements pub/sub messaging patterns for inter-component communication and connects to enterprise systems including accounting, compliance, and analytics.
An event-driven architecture is employed for payment orchestration, managing communication via a publish/subscribe (pub/sub) pattern. This architecture sustains persistent connections, thereby enhancing the performance of end-to-end real-time payment processing.
The event-driven architecture for real-time payment processing enables multiple payment operations to execute simultaneously using various adaptors, unlike traditional systems where processes are sequential and flow through a single pipeline. Payment events are distributed to specialized payment processor microservices according to their function (initiation, execution, tracking, settlements), allowing each to process independently without waiting for others.
As the transition moves from sequential to distributed processing, maintaining transaction traceability becomes crucial. The payment tracking adapters, as depicted in the diagram, connect to enterprise analytics systems, forming a specialized layer for transaction monitoring. The pub/sub model facilitates attaching correlation IDs to events, allowing systems to track related events across various topics and processing stages.
A standardized event schema forms the basis of this architecture, ensuring consistency across regional deployments while permitting customization at the adapter level. This schema defines uniform event structures that include tenant-specific metadata and supports versioning to adapt to evolving requirements. By confining region-specific variations to the adapter layer, the solution preserves core functionality while integrating with diverse enterprise systems through configuration-driven customization, rather than extensive code modifications.
For most payment processes, particularly those with independent processing steps that can run in parallel, this architecture yields net performance gains despite the topic switching overhead. This is especially true for complex transactions requiring multiple independent validations or processing steps.
Deployment on the AWS Cloud
The solution utilizes edge-optimized Amazon API Gateway for channels. An edge-optimized API endpoint directs requests to the closest Amazon CloudFront Point of Presence (POP). This approach is beneficial for geographically distributed clients, enabling efficient routing within each region, improving global responsiveness by reducing network round trips, and ensuring requests follow the shortest path before moving from the public internet to the client network.
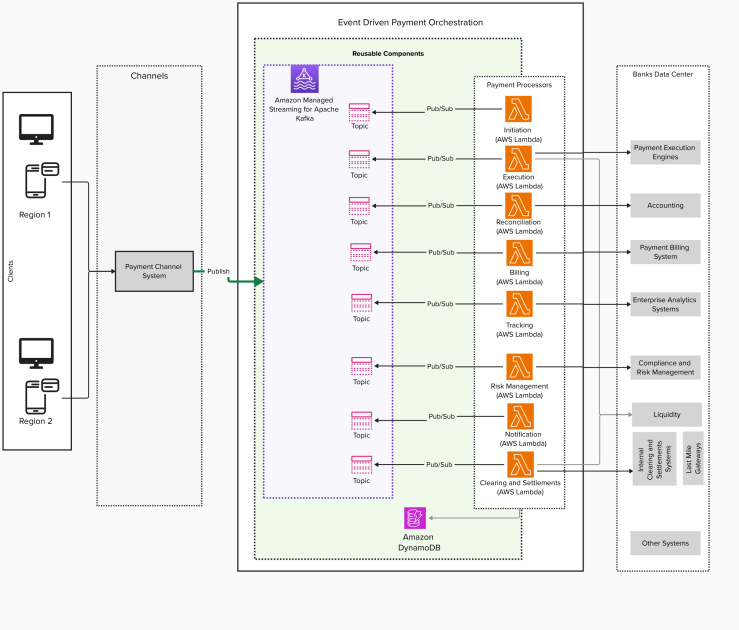
The diagram below illustrates the high-level solution architecture for real-time payments.

Comprehensive AWS payment orchestration solution implementing modern cloud-native architecture principles. Core processing logic implemented as Lambda functions covering initiation, execution, reconciliation, billing, tracking, risk management, and settlement workflows. Leverages Amazon MSK for reliable event streaming between components, with dedicated Kafka topics for each processing stage. Data persistence handled by Amazon DynamoDB, supporting cross-region operations. Architecture demonstrates AWS best practices for financial services, including regional redundancy, serverless computing, managed services, and event-driven design patterns. System integrates with external banking infrastructure and enterprise systems while maintaining separation of concerns through microservices architecture. Features built-in support for compliance monitoring, risk management, and payment tracking through specialized Lambda functions.
The solution employs Amazon MSK to establish an event-driven architecture, effectively managing both inbound and outbound channel traffic via API requests and asynchronous message-based events. Amazon MSK facilitates communication using a high-performance binary protocol among producers, consumers, and brokers, ensuring low latency and high throughput. Real-time payments are logically partitioned across multiple tenants within geographical regions, including North America, EMEA, LATAM, and Asia-Pacific.
Each real-time payment tenant adopts an active/active disaster recovery strategy by deploying MSK clusters across multiple AWS Regions, aiming for high availability and resilience. Amazon MSK provides both serverless and provisioned cluster options, allowing selection based on non-functional requirements and team expertise. Amazon MSK automatically manages partition leadership, with leaders in primary Regions and followers in secondary Regions. During failover, leaders are re-elected in healthy Regions, which helps maintain processing capabilities during regional incidents. Sticky partitioning uses consistent hashing for deterministic routing, and cooperative rebalancing enables efficient failover. Multi-AZ deployment offers zone redundancy and isolated clusters per Region for data sovereignty compliance through programmatic AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and virtual private cloud (VPC) boundaries.
To enable seamless cross-Region replication and ensure message continuity, Amazon MSK Replicator—a fully managed feature of Amazon MSK—is utilized. It replicates topics and synchronizes consumer group offsets across clusters. MSK Replicator streamlines the development of multi-Region Kafka applications by eliminating the need for custom code, open-source tool configuration, or infrastructure management. It automatically provisions and scales resources, allowing teams to concentrate on business logic while paying only for replicated data. In the event of a regional outage or failover, traffic can be automatically rerouted to a healthy Region without data loss or service disruption, achieving near-zero Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and uninterrupted operations for downstream services like payment processors and audit trail consumers.
Beyond regional redundancy, the architecture leverages an event-driven approach to facilitate parallel and decoupled processing of payment transactions. Events like transaction initiation, validation, and settlement are emitted asynchronously and consumed independently by various microservices, significantly reducing end-to-end latency.
To process these events at scale, the architecture can incorporate AWS Lambda, Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS), or Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS), depending on non-functional requirements. Automatic scaling responds to Amazon CloudWatch metrics, and exponential backoff retry logic with dead-letter queues (DLQs) manages throttling scenarios. Circuit breakers are implemented to prevent cascade failures during periods of high error rates.
A significant advantage of this solution is the reusability of payment flows across various regions. While each region possesses unique compliance requirements and settlement rules, the core functionalities of real-time payments (authorization, processing, settlement, and clearing) remain largely consistent. This reusability facilitates the rapid deployment of payment solutions in new regions without requiring a complete system rearchitecture. For instance, real-time payment systems in the US and UK might share similar business logic for real-time gross settlement but have different clearing and compliance requirements. The solution addresses these as bounded contexts within the microservices architecture, offering flexibility while ensuring each region can manage its specific rules and regulations.
Sustainability
AWS continuously innovates its infrastructure design, build, and operations to advance towards net-zero carbon by 2040 and achieve water positive status by 2030. Amazon MSK, when utilizing AWS Graviton-based instances, consumes up to 60% less energy than comparable M5 instances, supporting sustainability objectives. AWS Lambda is inherently sustainable by design. Its serverless model ensures compute resources are only active when necessary, significantly reducing idle infrastructure and wasted energy. Rather than maintaining always-on servers for infrequent tasks, Lambda provisions compute power just-in-time, resulting in near-zero idle capacity.
Security and compliance in financial services
Considering the sensitive nature of payment transactions and financial data, it is essential to implement security controls that comply with financial regulations such as AWS PCI DSS and AWS Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-3, tailored to organizational requirements.
The solution should integrate multi-layered security controls, continuous monitoring, and automated compliance auditing to satisfy the strict expectations of banking regulators and internal risk teams. Additional information can be found in the Security Guidance.
Conclusion
Modernizing payment orchestration systems with an event-driven architecture and AWS serverless technologies represents a significant step forward in addressing the demands of today’s rapidly changing financial services sector. This solution tackles the primary challenges of traditional payment systems, offering substantial advantages in performance, scalability, cost optimization, global resilience, sustainability, and compliance. By leveraging advanced cloud technologies and strong security controls, financial institutions can establish a future-proof foundation that adapts to evolving business needs while upholding the highest standards of performance, security, and reliability. As the real-time payments market experiences continued rapid growth, this modern architecture provides a solution that not only meets current demands but is also well-prepared to support future payment innovations. Organizations aiming to modernize their payment infrastructure can utilize this blueprint to accelerate their digital transformation, fostering sustainable, secure, and efficient payment processing at scale within an increasingly competitive global marketplace.