The Domain Name System (DNS) is a fundamental, yet often overlooked, component of internet usage. It functions by converting human-readable domain names, such as google.com, into numerical IP addresses like 142.250.217.78. Without DNS, devices would be unable to locate and exchange data across the internet.
Most home networks use a DNS server provided by their internet service provider (ISP). However, these default servers may not always offer optimal speed and could, in some instances, allow for tracking of online activities. For users prioritizing internet speed and privacy, adjusting DNS server settings is a worthwhile consideration.
Related: How to block ads across your entire Wi-Fi network with a Raspberry Pi
The most efficient way to alter your DNS server is at the router level, which will apply the changes to every device connected to that network. This setting is typically found within the LAN or DHCP sections of your router’s administration page.
If router access is restricted or unavailable, DNS settings can be modified individually on each device.
Key Sections:
How to change DNS settings at the router level
While individual devices can be configured to use a specific DNS server, modifying the settings at the router level is generally simpler. This approach ensures that all devices connected to the router automatically use your chosen DNS server. It is important to note that not all routers, particularly those supplied by ISPs, permit this setting to be changed. Nevertheless, it is worth attempting.
To begin, access your router’s administrative page. This is usually done via a web browser or a dedicated mobile app. For browser access, common IP addresses include 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, often with “admin” as both the default username and password. If these credentials do not work, a quick online search for your specific router model should provide the correct login details.
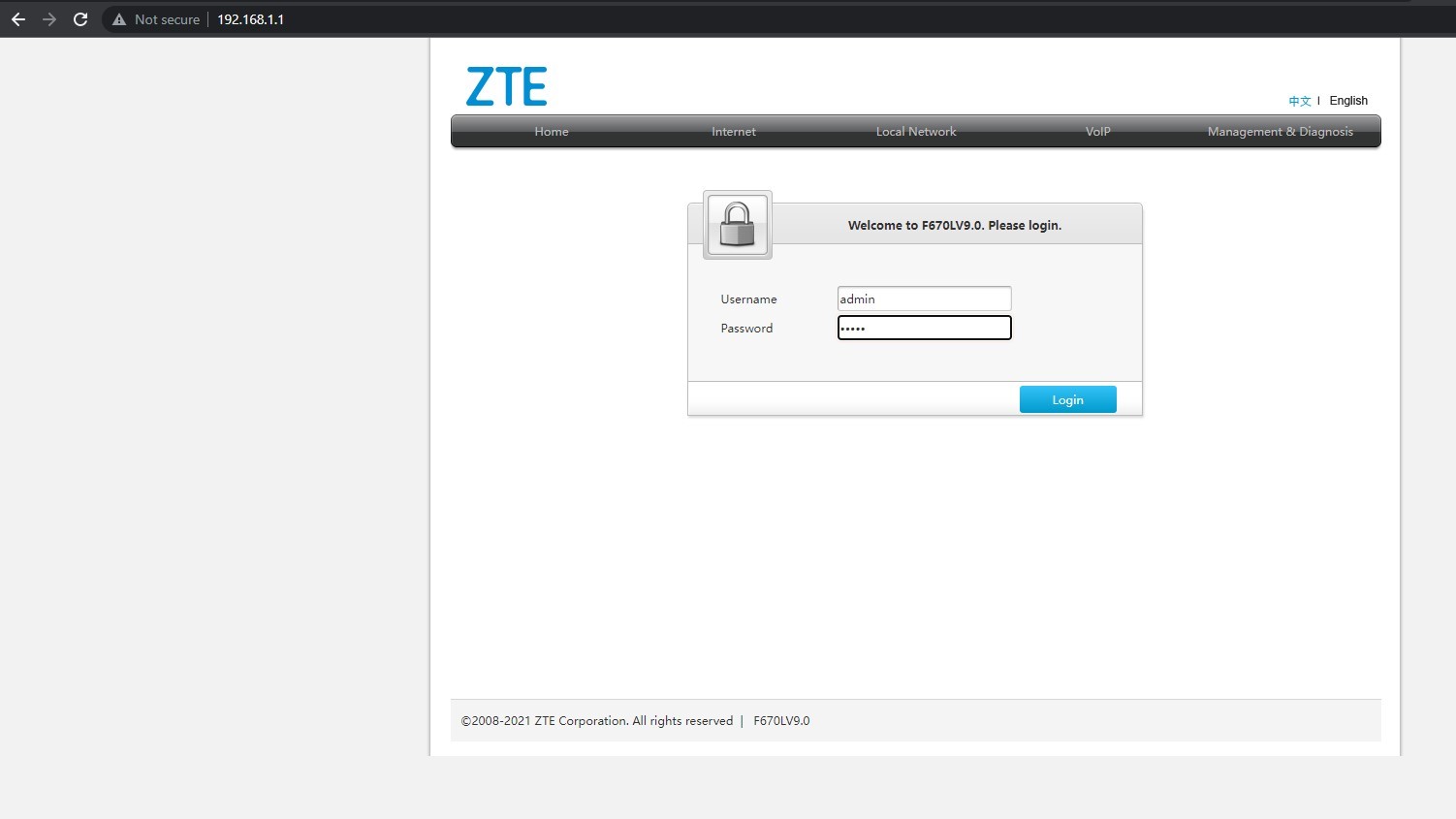
Once logged in, navigate to your router’s admin panel.

Look for DNS settings, typically under the Local Network or LAN sub-menu.
Assuming you have successfully logged in, here are the remaining steps:
- Enter the Network, Internet, or LAN menu. The exact label may differ depending on your router’s manufacturer.
- Find the DNS Address field. This might be located within an Advanced sub-menu.
- Enable the Use the following DNS address option. This will allow you to input your preferred primary and secondary DNS addresses.
- Click Save or Apply, then restart the router for the changes to take effect.
How to change DNS settings in Windows 11
If router control is not an option, DNS settings can still be adjusted on a per-device basis. Here is how to do it on Windows:
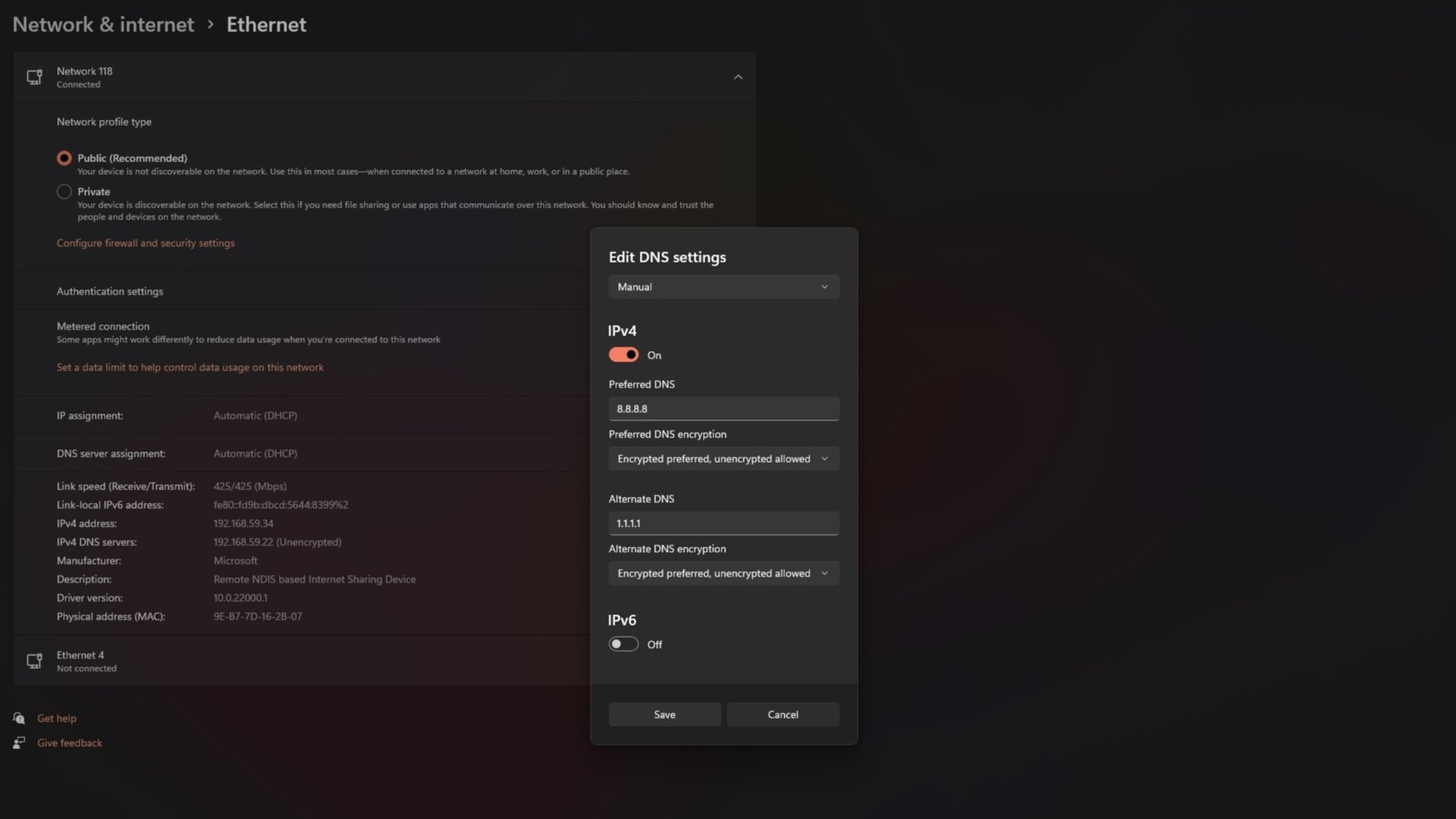
- Open the Settings app by using the Start menu or the Start+I keyboard shortcut.
- Navigate to Network and Internet on the left, then select either the Ethernet or Wi-Fi sub-menu, depending on your connection type.
- On the subsequent screen, locate the DNS server assignment field and click its Edit button. If using Wi-Fi, this field might be under Hardware properties.
- Change the Automatic (DHCP) DNS setting to Manual and activate the IPv4 toggle.
- Enter your preferred and alternate DNS addresses.
- Click Save to confirm the changes.
How to change DNS settings on a Mac
To modify DNS settings on a Mac, click the Apple menu in the top-left corner of the screen and open System Preferences. Then, proceed with these steps:

- From the categories list, select Network.
- Choose the network type for which you want to change DNS settings, either Wi-Fi or Ethernet/LAN.
- Click Advanced and switch to the DNS tab.
- Click the + icon to add a DNS server. Input the desired IP address, such as 8.8.8.8.
- Click OK and then Apply to save the changes.
How to change DNS settings on Android
Adjusting your DNS server on Android has become straightforward since Android 9 Pie. Follow these steps:

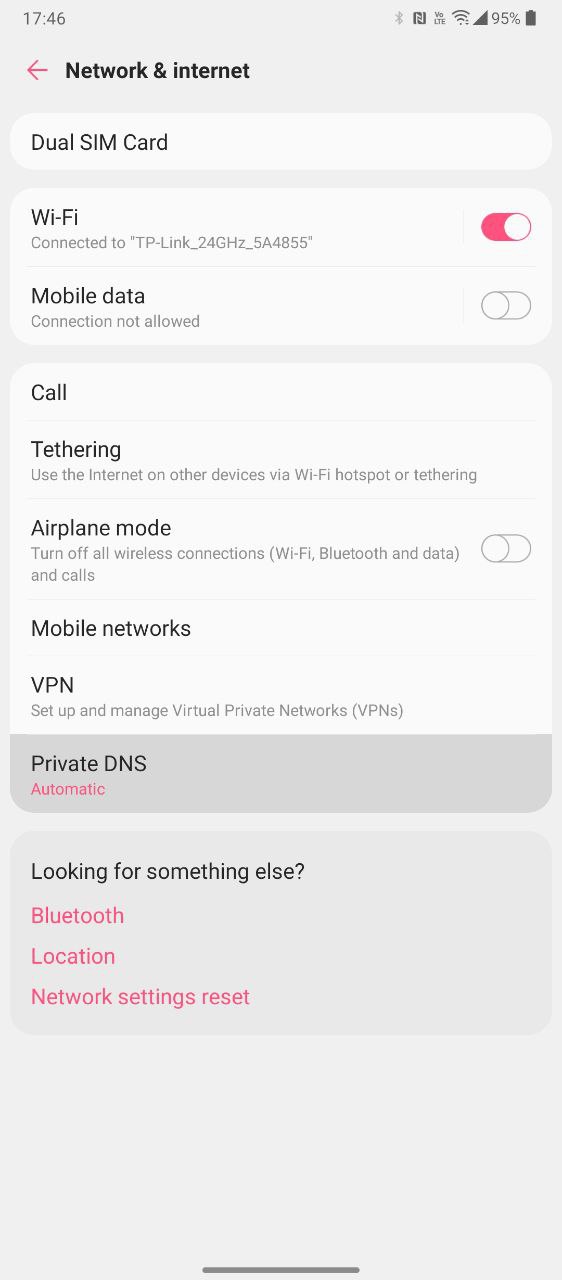
- Open Settings, then access the Network & Internet sub-menu.
- Tap Private DNS. This option might be located under an Advanced sub-menu on some devices.
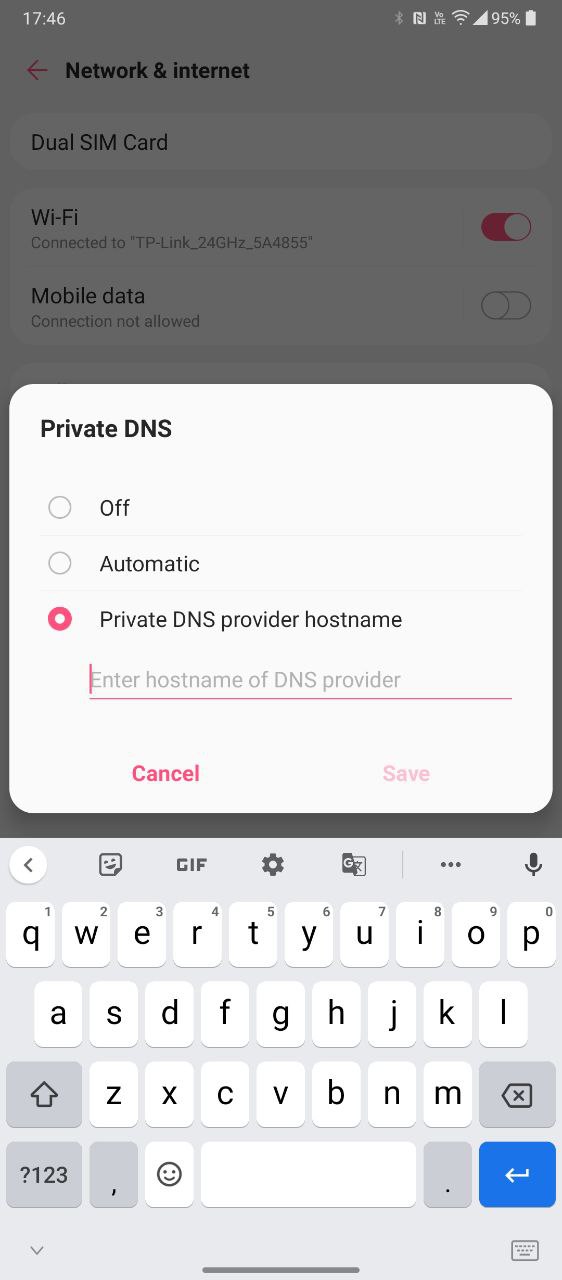
- Change the default Automatic selection to “Private DNS provider hostname” and enter your custom DNS address.
It is important to note that Android’s Private DNS feature requires a domain (hostname) like 1dot1dot1dot1.cloudflare-dns.com instead of an IP address such as 1.1.1.1. Not all DNS providers offer a hostname for this purpose.
How to change DNS settings on an iPhone or iPad
To change the preferred DNS server on an iOS device like an iPhone or iPad, follow these instructions:

- Open the Settings app.
- Enter the Wi-Fi sub-menu and select your current network from the list.
- Under the DNS section, tap “Configure DNS” and change the selection from Automatic to Manual.
- Remove any existing DNS servers and tap the + icon to add your own.
- Tap Save and repeat this process for any other Wi-Fi networks you frequently use.
Note that iOS does not permit the use of a specified DNS server for cellular connections. A third-party application, such as Cloudflare Warp, can bypass this limitation by establishing an always-on VPN connection.
Further reading: What is a VPN? Do you need one?
How to change DNS settings on a Chromebook
Similar to Android, ChromeOS offers an easy way to change your DNS server. Simply follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app, accessible from either the quick settings or search menu.
- Select the connection for which you wish to change the DNS servers, whether it is Wi-Fi, mobile network, or Ethernet.
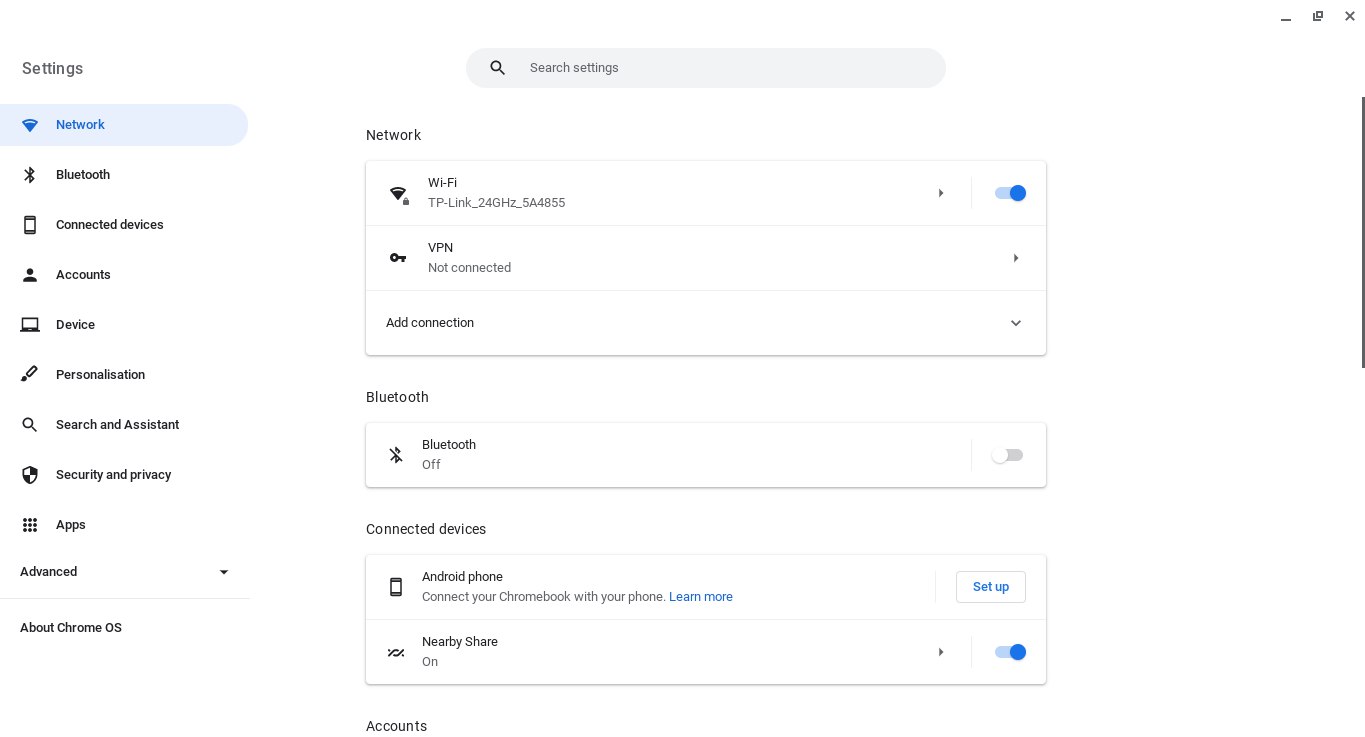
- Choose your current network and navigate to the Network > Advanced sub-menu.
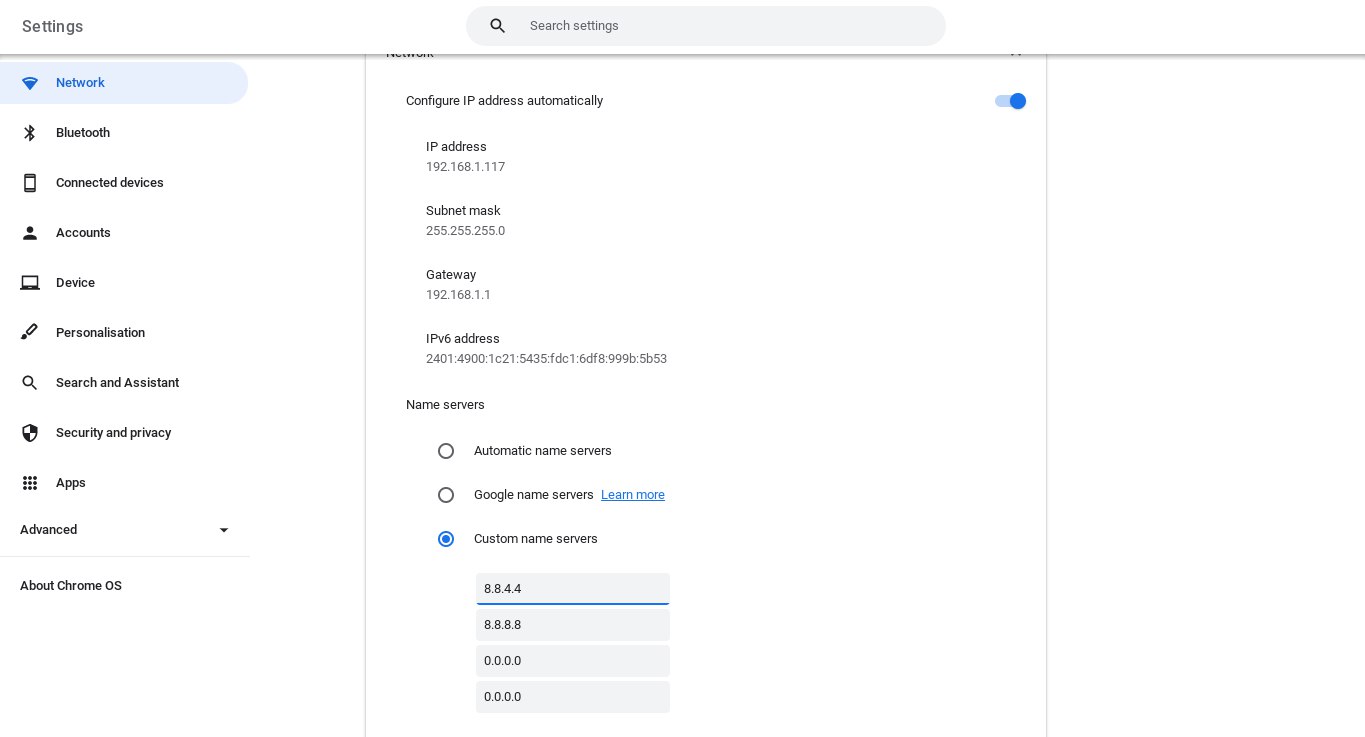
- Scroll down to the Name servers section and change the Automatic selection to Custom name servers. You can then input your preferred DNS provider’s IP address.
Also see: How to set up a VPN on Android, Windows, and other platforms


