Grand Theft Auto 6 and the Future of AI
The recent reveal of
for Grand Theft Auto 6 captivated audiences, showcasing a title that appears groundbreaking on multiple fronts. However, GTA 6 might represent the pinnacle of traditional open-world game design, potentially preceding a significant shift driven by generative AI.
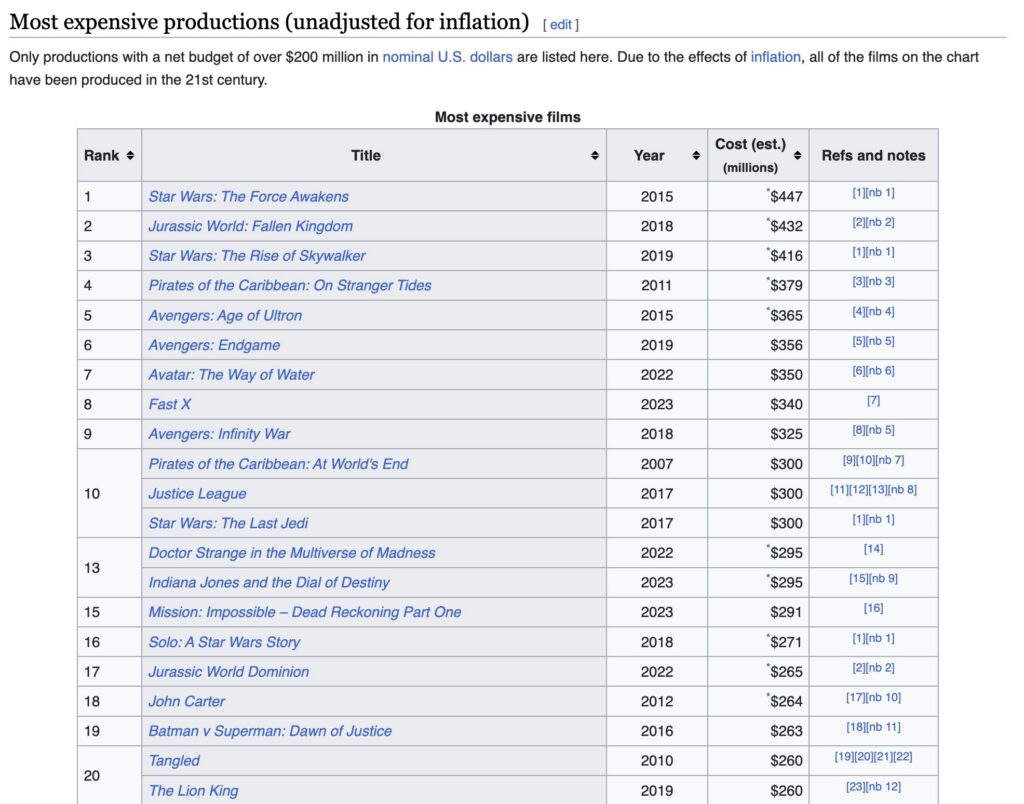
Remarkably, GTA 6 carries an estimated budget of $1-2 billion, establishing it as THE MOST EXPENSIVE GAME EVER developed. This figure dwarfs the budgets of even the biggest Hollywood blockbusters, such as modern Star Wars, Avengers, or Pirates of the Caribbean films, which typically range from $300-450 million. This makes GTA 6 nearly five times more costly.

This immense investment underscores the increasing cultural prominence of gaming. The game’s trailer quickly became the most-viewed non-music video on YouTube within 24 hours of its release, surpassing movie trailers, TV show premieres, and even popular content creators like MrBeast. It garnered 70 million views in its first 10 hours and exceeded 140 million views within a few weeks.

The development process for GTA 6 contrasts sharply with the rapid iteration often seen in the tech industry. Instead of a ‘move fast and break things’ approach, this game:
- Required an estimated $1-2 billion in funding.
- Began development in 2014, projecting an 11-year journey to release.
- Involved thousands of developers, designers, and other professionals working intensely to complete it.
Despite this traditional development model, the tools and methodologies for creating games are undergoing rapid transformation.
How Generative AI is Reshaping the Games Industry
Generative AI is beginning to influence various aspects of game development. While still in its early stages, its impact is being observed across multiple areas, from initial concept art to in-game assets and NPC interactions:
- Producing endless variations of concept art.
- Designing and creating 3D assets.
- Powering NPCs with large language models (LLMs).
- Generating diverse environments and entire worlds.
- Synthesizing speech for in-game characters.
- Developing bots for competitive play and onboarding in PvP games.
- Creating infinite quests and narrative storylines.
- And more.
These represent the “weak form” innovations, which are readily conceivable today. As described by Chris Dixon, weak form technologies often appear alongside a “strong form” counterpart. While the weak form is more easily understood by the market, the strong form typically delivers a more profound impact.
The “strong form” of AI innovation is expected to influence open-world games like GTA in more emergent ways. For instance, the modding community previously enabled the rise of GTA RP (role-play), fostering new gameplay where players assume roles such as police officers or gang leaders. Millions have engaged in this format, and even more have watched, demonstrating a novel and inventive style of play that did not exist before.

A similar evolution is anticipated for future iterations of the open-world genre. Generative AI will likely reduce development costs for games like GTA or enable more content creation within existing budgets. Crucially, AI is also expected to unlock entirely new forms of gameplay.
Consider the potential of an AI-powered ‘town’ within a GTA-like environment, where NPCs possess individual inner thoughts, motivations, and needs. This underlying platform could facilitate next-generation social or dating experiences. Open-world games might evolve into something akin to a physics engine, augmented with layers of modding and AI. Such expansive playgrounds could even host a multitude of other game genres within them, similar to platforms like Roblox.
Generative AI: Reinventing Genres, Not Just Reducing Costs
Reflecting on past content revolutions, platforms like YouTube and TikTok dramatically lowered the cost of video creation for users. However, creators did not simply use this technology to mimic Hollywood productions. Instead of competing with two-hour films or ten-episode TV series, entirely new video formats emerged, native to the digital medium. Examples include personality-driven vlogging, video game streaming, and long-form podcasts. These formats offer entertainment through different approaches, often assembling hours of content from short, engaging segments.
While the discussion often centers on large open-world games, the most innovative new experiences may not resemble Grand Theft Auto at all. Instead, new game genres could emerge rapidly, competing in novel ways:
- Games as a new meme format: Imagine a humorous political debate moment inspiring a fully-fledged fighting game, built using no-code, AI-enabled tools, that becomes a viral hit the same evening.
- Ultra-personalized gaming: Individuals could create vast, immersive, and deep games specifically for a small group, such as a 50-person college club, simply because the tools make it feasible.
- Gaming integrated with commerce and other experiences: Currently, developing a massive game to accompany a major franchise like Harry Potter is economically viable. However, if content creation costs approach zero, it might become feasible to create rich gaming experiences to promote even a small e-commerce store.
Ultimately, the traditional model for developing a high-budget game like GTA is likely to change significantly. Future content, quests, and potentially even entire genres could be generated by AI, leading to experiences that may not align with current definitions of a ‘game.’
The past year has been a period of exploration for the games industry, but it remains very early. Experimentation is widespread, and some tools, like Midjourney for concept art, have gained traction. However, widespread AI integration into production pipelines is still limited. A major transformation is on the horizon, promising a wave of change as significant as any previously witnessed in this industry.