Experiencing microstutters in games, occasional hitches, or a general lack of responsiveness when opening applications on your Windows PC? While various factors can contribute to these issues, your power settings are a crucial area to investigate. Even with high-end components, optimal performance requires a consistent power supply, making it essential to ensure your system isn’t being held back by overly restrictive power management.
Windows Prioritizes Power Efficiency Aggressively
Balancing Green Initiatives with Performance Needs
Technology companies, including Microsoft, have increasingly focused on energy efficiency. This commitment is evident in features like energy-aware downloading on Xbox Series consoles. As Windows is a widely used operating system, Microsoft dictates its default power management. While saving a few watts across millions of computers significantly reduces energy consumption and environmental impact, these power-saving measures can become counterproductive if they negatively affect user experience and system performance.
“Balanced” Power Mode May Not Be Truly Balanced
Default Settings Often Favor Power Saving Over Performance
Windows typically offers three power presets: Best Power Efficiency, Balanced, and Best Performance.  These might also be labeled “Power Saving,” “Balanced,” and “High Performance,” depending on your Windows version. These options are accessible via Settings > System > Power & Battery or Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Power Options. While the “High Performance” preset might not always be visible, it’s not essential for optimizing performance. The “Balanced” mode is usually the default, designed to provide necessary performance while conserving power during idle periods by parking CPU cores or putting USB devices to sleep. However, in practice, the current “Balanced” setting often leans too heavily towards power saving, leading to noticeable performance drawbacks.
These might also be labeled “Power Saving,” “Balanced,” and “High Performance,” depending on your Windows version. These options are accessible via Settings > System > Power & Battery or Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Power Options. While the “High Performance” preset might not always be visible, it’s not essential for optimizing performance. The “Balanced” mode is usually the default, designed to provide necessary performance while conserving power during idle periods by parking CPU cores or putting USB devices to sleep. However, in practice, the current “Balanced” setting often leans too heavily towards power saving, leading to noticeable performance drawbacks.
Aggressive Power Management Can Disrupt Real-Time Workloads
Identifying Performance Issues Caused by Power Settings
When a CPU reduces its clock speed or parks cores for power saving, there’s a brief delay as it ramps back up to full speed. This delay manifests as increased system latency, which can be monitored using tools like LatencyMon.  Such power-related issues can cause stutters in video games, Bluetooth device disconnections, and audio glitches like pops and crackles. These problems can render a computer frustrating to use, impacting latency-sensitive operations such as USB device communication, audio playback, network performance, and even game input responsiveness, even if average frame rates appear stable.
Such power-related issues can cause stutters in video games, Bluetooth device disconnections, and audio glitches like pops and crackles. These problems can render a computer frustrating to use, impacting latency-sensitive operations such as USB device communication, audio playback, network performance, and even game input responsiveness, even if average frame rates appear stable.
Optimizing Power Settings for Enhanced PC Performance
Adjusting Key Settings for a More Responsive System
To address these performance issues, it’s important to note that these adjustments are primarily for desktop PCs or laptops when plugged into a power source. Modifying power settings on a laptop running on battery is generally not recommended. Begin by opening the Start Menu and searching for “Edit Power Plan.” Select this option. 
Next, click on “Change advanced power settings.” 
Within these advanced settings, focus on the “Plugged in” options. Navigate to Processor power management > Minimum processor state and change the “Plugged in” value from 5% to 10%. 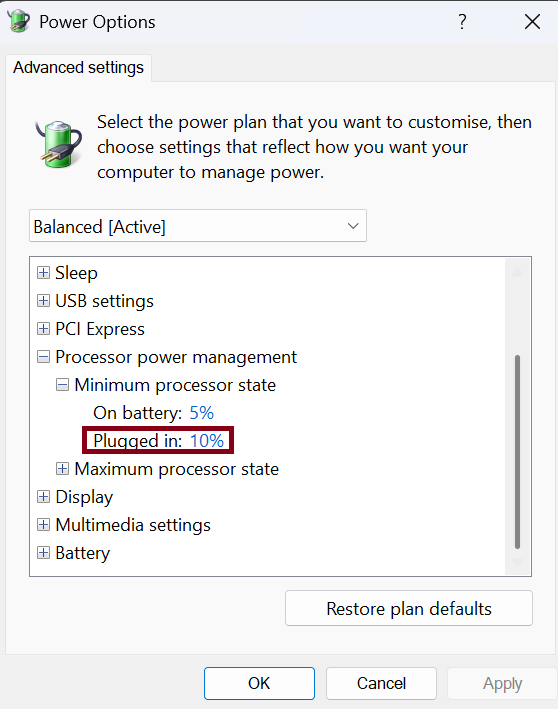
This adjustment prevents the CPU from entering overly aggressive low-power states when idle, which can introduce latency when the system needs to ramp up quickly. While the effectiveness may vary across different CPUs, this change often reduces latency. If issues persist, you might incrementally increase this value, but be mindful that higher percentages can lead to increased heat and fan noise.
Next, locate PCI Express > Link State Power Management and set the “Plugged in” option to “Off.”  This prevents the PCIe bus from entering low-power states, which can reduce latency for GPUs and SSDs, smoothing out performance spikes without necessarily boosting maximum frame rates.
This prevents the PCIe bus from entering low-power states, which can reduce latency for GPUs and SSDs, smoothing out performance spikes without necessarily boosting maximum frame rates.
Proceed to USB Settings > USB selective suspend setting and set it to “Disabled” for the “Plugged in” state. 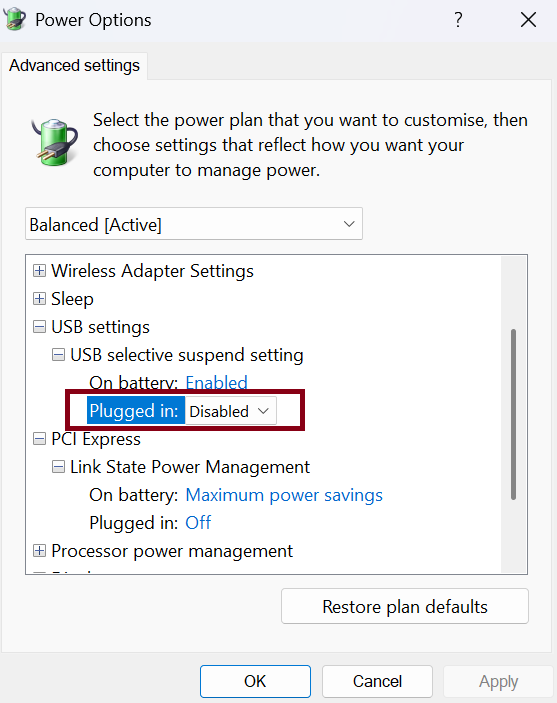
Finally, navigate to Wireless Adapter Settings > Power Saving Mode and select “Maximum Performance” for the “Plugged in” setting. This ensures your Wi-Fi adapter remains fully active and doesn’t enter a sleep mode when idle. 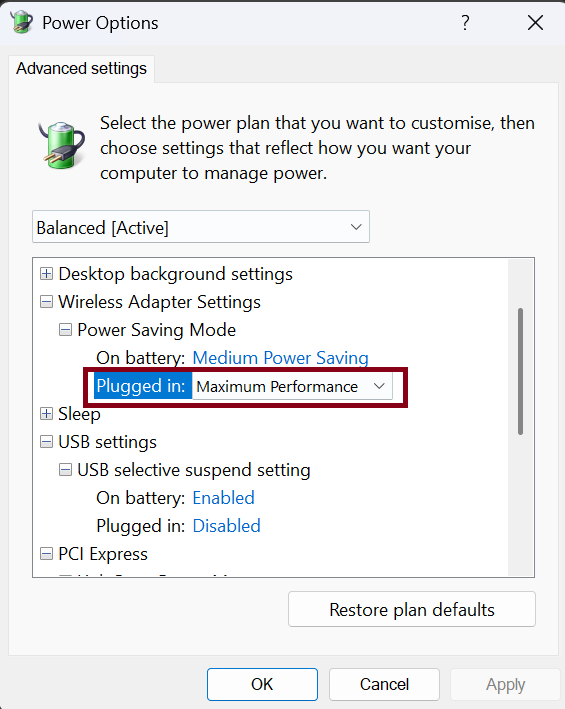
It is important to understand that these modifications will likely increase your PC’s power consumption, potentially leading to higher idle temperatures and increased fan noise. However, the benefit is a more responsive and reliable computing experience. The decision to implement these changes depends on whether the performance gains outweigh these potential trade-offs for your specific use case.


