Message processing systems are essential for organizations to prioritize critical business operations while efficiently managing routine tasks. Urgent messages, such as rush orders, critical system alerts, or multi-step business processes, often require immediate attention, while other routine requests must still be processed reliably.
This article demonstrates how to construct a priority-based message processing system utilizing Amazon MQ for priority queuing, Amazon DynamoDB for data persistence, and AWS App Runner for serverless compute. The approach includes implementing application-level delays that high-priority messages can bypass, establishing real-time user interfaces with WebSocket connections, and configuring dual-layer retry mechanisms to ensure maximum reliability.
This solution addresses three key challenges in modern data processing:
- Implementing configurable delay processing at the application level
- Supporting priority-based message routing that respects business requirements
- Providing real-time feedback to users through WebSocket connections
Leveraging AWS managed services helps reduce operational complexity, allowing teams to concentrate on business logic instead of infrastructure management. Priority-based message handling ensures that critical operations receive prompt attention, while routine tasks are processed efficiently in the background. Users benefit from status updates that offer visibility into their requests, and retry mechanisms enhance reliability during potential failures. An infrastructure as code (IaC) approach facilitates consistent deployments across various environments, from development to production.
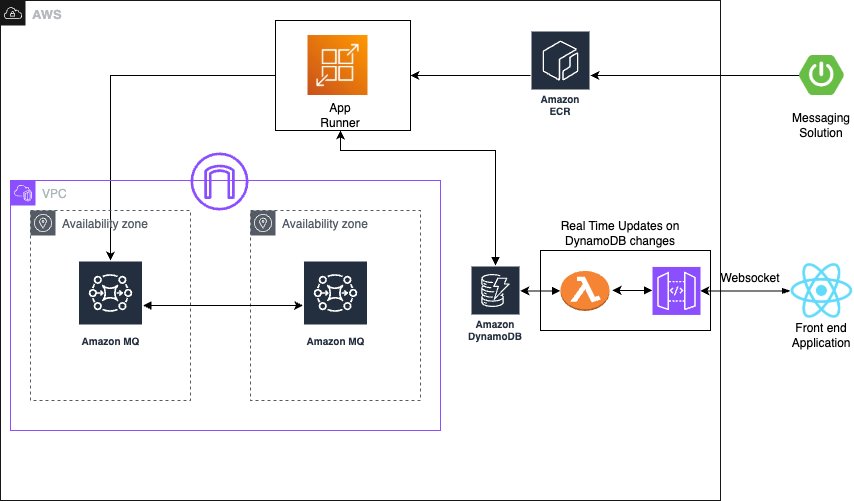
Solution overview
The solution integrates several AWS managed services to create a serverless, priority-based message processing system with real-time user feedback. The architecture implements intelligent routing based on three message priority levels, ensuring critical messages receive immediate processing:
- High-priority path – Messages bypass delays and queue immediately with JMS priority 9
- Standard-priority path – Messages undergo configured delays before queuing with JMS priority 4
- Low-priority path – Messages process after all higher priority messages with JMS priority 0
The following diagram illustrates this architecture.

The solution utilizes the following AWS managed services to deliver a scalable, serverless architecture:
- AWS App Runner is a fully managed container application service that automatically builds, deploys, and scales containerized applications. It provides automatic scaling based on traffic, built-in load balancing and HTTPS, seamless integration with container registries, and zero infrastructure management overhead.
- Amazon MQ is a managed message broker service for Apache ActiveMQ that offers priority-based message queuing, automatic failover for high availability, message persistence and durability, and JMS protocol support for enterprise applications.
- Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service providing single-digit millisecond performance at any scale, automatic scaling with on-demand pricing, built-in security and backup capabilities, and global tables for multi-Region deployments.
The system employs JMS priority levels with High=9, Medium=4, and Low=0 for automatic ordering, combined with conditional delay processing based on priority classification. Amazon MQ provides reliable message delivery and persistence with dead-letter queue (DLQ) configuration for handling failed messages.
Asynchronous delay processing uses CompletableFuture implementation for non-blocking delays, thread pool management for concurrent processing, graceful error handling with retry mechanisms, and configurable delay periods per message type to optimize resource utilization. For real-time status updates, the solution provides WebSocket connections for bidirectional communication, Amazon DynamoDB Streams for change data capture (CDC), comprehensive status tracking throughout the processing lifecycle, and a React frontend integration for live updates, ensuring users have complete visibility into their message processing status.
The standard priority messaging flow (shown in the following diagram) handles messages with configurable delays using JMS asynchronous processing capabilities. Messages wait for their specified delay period before entering the Amazon MQ queue, where they are then processed.

The high-priority messaging flow (shown in the following diagram) offers an express lane for critical messages. These messages bypass the delay mechanism entirely and proceed directly to the queue, enabling immediate processing for time-sensitive operations.

To simplify getting started, an example application is available to observe Amazon MQ behavior with varying message volumes. The source code repository, IaC implementation, and instructions to run the sample can be found on GitHub.
The following sections detail the deployment of the complete processing system.
Prerequisites
To successfully deploy the priority-based message processing system, ensure the following tools, permissions, and knowledge are in place. An active AWS account with the following configurations is required:
- The AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) version 2.15.0 or later
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles with the minimum permissions:
# JSON
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"apprunner:CreateService",
"apprunner:UpdateService",
"apprunner:DeleteService"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:apprunner:*:*:service/reactive-demo-*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"mq:SendMessage",
"mq:ReceiveMessage",
"mq:DeleteMessage"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:mq:*:*:broker/reactive-demo-broker/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:UpdateItem",
"dynamodb:Query"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:*:*:table/reactive-items*"
}
]
}Install and configure the following development tools on your local machine:
- Java 17 or later
- Spring Boot 3.2.0 or later
- Node.js 18.19.0 or later
- Docker 24.0.7 or later
- Maven 3.9.6 or later
- AWS CDK 2.124.0 or later
Basic familiarity with the following is recommended for successful implementation of this solution:
- Spring Boot applications
- Message queue concepts
- WebSocket protocols
- React development
Configure the infrastructure stack
This step involves creating the core AWS services using the AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK). This modular approach enables independent stack management and environment-specific configurations.
- Create a new AWS CDK project:
# Bash
mkdir priority-processing && cd priority-processing
cdk init app --language python
pip install aws-cdk-lib constructs- Create the infrastructure stack:
# Python
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_dynamodb as dynamodb,
aws_amazonmq as mq,
aws_kms as kms,
Duration,
RemovalPolicy,
CfnOutput
)
from constructs import Construct
class MessageProcessingStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
# Create KMS key for encryption
self.kms_key = kms.Key(
self, "ProcessingKey",
description="Key for message processing encryption",
enable_key_rotation=True
)
# DynamoDB table with comprehensive configuration
self.items_table = dynamodb.Table(
self, "ItemsTable",
table_name="reactive-items",
partition_key=dynamodb.Attribute(
name="id",
type=dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING
),
stream=dynamodb.StreamViewType.NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES,
billing_mode=dynamodb.BillingMode.ON_DEMAND,
encryption=dynamodb.TableEncryption.CUSTOMER_MANAGED,
encryption_key=self.kms_key,
point_in_time_recovery=True,
removal_policy=RemovalPolicy.DESTROY
)
# Add Global Secondary Index for status queries
self.items_table.add_global_secondary_index(
index_name="StatusIndex",
partition_key=dynamodb.Attribute(
name="status",
type=dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING
),
sort_key=dynamodb.Attribute(
name="createdAt",
type=dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING
)
)
# Amazon MQ broker configuration
self.mq_broker = mq.CfnBroker(
self, "MessageBroker",
broker_name="reactive-demo-broker",
engine_type="ACTIVEMQ",
engine_version="5.18",
host_instance_type="mq.t3.micro",
deployment_mode="SINGLE_INSTANCE",
publicly_accessible=False,
logs=mq.CfnBroker.LogListProperty(
audit=True,
general=True
),
encryption_options=mq.CfnBroker.EncryptionOptionsProperty(
use_aws_owned_key=False,
kms_key_id=self.kms_key.key_id
),
users=[mq.CfnBroker.UserProperty(
username="admin",
password="SecurePassword123!",
console_access=True
)]
)
# Output values for application configuration
CfnOutput(self, "TableName",
value=self.items_table.table_name,
description="DynamoDB table name")
CfnOutput(self, "MQBrokerEndpoint",
value=self.mq_broker.attr_amqp_endpoints[0],
description="Amazon MQ broker endpoint")- Run the following commands to deploy the stack:
# Bash
cdk bootstrap
cdk deploy MessageProcessingStackThe infrastructure can be verified on the AWS Management Console.
Configure the message processing application
In this step, the Spring Boot application is created with priority-based message processing capabilities. First, the application.properties file is configured to incorporate environment variables, including AWS credentials, AWS Regions, and other configuration parameters such as log levels into the application and business logic implementation. Next, the message service is implemented using a JMS template with comprehensive error handling, followed by enhancing the JMS configuration with connection pooling for improved performance.
The following code illustrates an example message service implementation:
// Example message service implementation
@Service
public class MessageService {
@Autowired
private JmsTemplate jmsTemplate;
public void sendPriorityMessage(Message message) {
jmsTemplate.send(session -> {
Message jmsMessage = session.createTextMessage(message.getContent());
jmsMessage.setJMSPriority(message.getPriority());
return jmsMessage;
});
}
}For proper timestamp update implementation, the DynamoDB SDK service is integrated with caching capabilities. Finally, after implementing the REST controller for the API with asynchronous processing support, the message processing application can be deployed. This implementation includes Java code application-level delay processing for demonstration purposes. While this approach effectively showcases the priority-based message routing capabilities and real-time WebSocket updates in a demo environment, AWS recommends using Amazon MQ delay processing features for production workloads. For production implementations, Amazon MQ delay and scheduling capabilities should be used instead of application-level delays, through features like Amazon MQ delay queues, ActiveMQ scheduling features, and appropriate message Time-to-Live (TTL) configurations.
The following code is an example snippet showcasing the Amazon MQ feature:
// Create connection factory with Amazon MQ endpoint
ActiveMQConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory(brokerUrl);
factory.setUserName("admin");
factory.setPassword("your-password");
try (Connection connection = factory.createConnection();
Session session = connection.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE)) {
// Create destination and producer
Destination destination = session.createQueue(queueName);
MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(destination);
// Create message
TextMessage message = session.createTextMessage(messageContent);
// Set native delay using ActiveMQ scheduled delivery
message.setLongProperty(ScheduledMessage.AMQ_SCHEDULED_DELAY, delayMillis);
// Optionally set priority for delayed message
message.setJMSPriority(4);
// Send the message - it will be delivered after the specified delay
producer.send(message);
}Build and deploy the Spring Boot application to App Runner
In this step, the application is pushed to Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) to run it in App Runner:
- Build and push the Docker image to Amazon ECR:
# Bash
# Build the Docker image
docker build -t reactive-demo .
# Create ECR repository
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name reactive-demo --region us-east-1
# Get login token and login to ECR
aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $ECR_URI
# Tag and push image
ECR_URI=$(aws ecr describe-repositories --repository-names reactive-demo --query 'repositories[0].repositoryUri' --output text)
docker tag reactive-demo:latest $ECR_URI:latest
docker push $ECR_URI:latest- Create the App Runner service with environment variables for the DynamoDB table and Amazon MQ broker endpoint:
# Python
from aws_cdk import (
aws_apprunner as apprunner,
aws_iam as iam
)
class AppRunnerStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, id: str,
table_name: str, mq_endpoint: str, **kwargs):
super().__init__(scope, id, **kwargs)
# Create IAM role for App Runner
app_runner_role = iam.Role(
self, "AppRunnerRole",
assumed_by=iam.ServicePrincipal("tasks.apprunner.amazonaws.com"),
managed_policies=[
iam.ManagedPolicy.from_aws_managed_policy_name(
"AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess"
),
iam.ManagedPolicy.from_aws_managed_policy_name(
"AmazonMQFullAccess"
)
]
)
# Create App Runner service
self.service = apprunner.CfnService(
self, "ReactiveProcessingService",
service_name="reactive-processing-service",
source_configuration=apprunner.CfnService.SourceConfigurationProperty(
authentication_configuration=apprunner.CfnService.AuthenticationConfigurationProperty(
access_role_arn=app_runner_role.role_arn
),
image_repository=apprunner.CfnService.ImageRepositoryProperty(
image_identifier=f"{ECR_URI}:latest",
image_configuration=apprunner.CfnService.ImageConfigurationProperty(
port="8080",
runtime_environment_variables=[
{"name": "DYNAMODB_TABLE_NAME", "value": table_name},
{"name": "MQ_BROKER_URL", "value": mq_endpoint}
]
),
image_repository_type="ECR"
)
),
health_check_configuration=apprunner.CfnService.HealthCheckConfigurationProperty(
path="/actuator/health",
protocol="HTTP",
interval=10,
timeout=5,
healthy_threshold=1,
unhealthy_threshold=5
),
instance_configuration=apprunner.CfnService.InstanceConfigurationProperty(
cpu="0.5 vCPU",
memory="1 GB"
)
)Set up real-time updates
For this step, WebSocket support for real-time status updates is implemented using AWS Lambda to process DynamoDB streams and send updates to connected clients using Amazon API Gateway WebSocket connections. The code snippet for this can be found at this link
Deploy the React application to Amazon S3 and Amazon CloudFront
In this step, a frontend application is created to enable the WebSocket connection for observing message updates in DynamoDB and API Gateway WebSocket connections.
Similar to the above section, the AWS CDK code for building the frontend is available for validating the solution.
Validate the solution
This section provides comprehensive testing procedures to validate the priority-based message processing system.
Automated testing script
After completing the preceding steps, a comprehensive testing script can be initiated to validate priority processing and delay behavior:
# Bash
#!/bin/bash
curl -X POST "$API_URL/api/items" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"title": "High Priority Task",
"priority": "High",
"delay": 10
}'Validation through the web interface
The following screenshot of the UI illustrates how the queueing mechanism can function with real-time updates using WebSockets.

The web interface provides validation of the priority-based message processing system. Access the Amazon CloudFront URL to view the following information:
- Real-time message processing with live status updates
- Queue statistics showing message distribution by priority
- Processing timeline demonstrating priority bypass behavior
- WebSocket connection status indicating real-time connectivity
Amazon CloudWatch dashboards and alarms
AWS recommends creating Amazon CloudWatch dashboards to track the priority-based message processing system’s performance across multiple dimensions. Message processing can be monitored by priority levels to ensure high-priority messages are processed first and to identify any bottlenecks in the priority routing logic. The following screenshot shows an example dashboard.

Queue depth and processing times can be tracked to understand system load and latency patterns, which helps optimize resource allocation and identify when scaling is necessary. DynamoDB performance metrics, including read/write capacity consumption, throttling events, and latency, should be observed to ensure the database layer maintains optimal performance under varying loads.

Additionally, implementing application-specific custom metrics such as message processing success rates, retry counts, and business-specific KPIs can provide deeper insights into the application’s behavior and support data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
Security considerations
AWS recommends implementing comprehensive security measures to safeguard the message processing system. This begins with implementing least privilege IAM policies that grant only the minimum permissions required for each component to function, ensuring services like App Runner can only access the specific DynamoDB tables and Amazon MQ queues they need. Network architecture should be configured using a virtual private cloud (VPC) with private subnets for Amazon MQ, isolating the message broker from direct internet access while maintaining connectivity through NAT gateways for necessary outbound connections.
Encryption at rest should be enabled using AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) for DynamoDB tables and Amazon MQ data, and encryption in transit should be enforced by configuring SSL/TLS connections for all service communications, particularly for ActiveMQ broker connections. Finally, security groups should be configured with minimal access rules that explicitly define allowed traffic between components, restricting inbound connections to only the ports and protocols required for the application to function, such as port 61617 for ActiveMQ SSL connections from App Runner instances.
Cost considerations
Cost estimates, based on the US East (N. Virginia) Region, indicate that actual costs may vary depending on the Region, usage patterns, and pricing changes. For a small workload (1,000 messages/day), estimated costs range from $5–10 for Amazon DynamoDB, $15 for Amazon MQ (t3.micro), $20–40 for AWS App Runner, $3–5 for Amazon API Gateway WebSocket, $5–10 for Amazon CloudWatch Logs, and $5 for Data Transfer, totaling an estimated $53–95. For a medium workload (10,000 messages/day), costs are estimated at $25–50 for DynamoDB, $30 for Amazon MQ (m5.large), $50–150 for App Runner, $10–25 for API Gateway WebSocket, $10–20 for CloudWatch Logs, and $10–20 for Data Transfer, resulting in a total estimated cost of $135–295. For a large workload (100,000 messages/day), estimates include $200–400 for DynamoDB, $120 for Amazon MQ (m5.xlarge), $400–800 for App Runner, $50–100 for API Gateway WebSocket, $30–50 for CloudWatch Logs, and $50–100 for Data Transfer, bringing the total estimated cost to $850–1,570.
Troubleshooting
The following are common issues and their solutions when implementing the priority-based message processing system:
- Messages not processing in priority order:
- Verify JMS priority is configured correctly: message.setJMSPriority(priority)
- Check ActiveMQ broker configuration for priority queue support
- Confirm CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE mode is properly configured
- Review queue consumer concurrency settings
- WebSocket updates not working:
- Verify DynamoDB Streams is enabled on the table
- Check the Lambda function is triggered by stream events
- Validate API Gateway WebSocket configuration and IAM permissions
- Test the WebSocket connection using browser developer tools
- Application scaling issues:
- Monitor App Runner metrics in CloudWatch
- Adjust auto scaling configuration based on traffic patterns
- Consider Amazon MQ broker capacity and upgrade if needed
- Review DynamoDB capacity settings and enable auto scaling
Clean up
To avoid incurring ongoing AWS charges, delete the resources created in this walkthrough:
- Delete the CDK stacks:
cdk destroy MessageProcessingStack
cdk destroy FrontendStack- Remove the App Runner service:
aws apprunner delete-service --service-arn <your-service-arn>- Delete the ECR repositories and container images.
- Remove CloudWatch log groups if not set to auto-delete.
- Delete S3 buckets used for frontend hosting.
Next steps
To extend this solution and add additional capabilities, consider the following enhancements:
- Integrate AWS Step Functions for complex workflow orchestration
- Add Amazon EventBridge for event-driven integrations
- Implement Lambda for serverless message processing
- Use Amazon SageMaker for ML-based priority classification
- Build dashboards with Amazon QuickSight for business intelligence
Conclusion
This solution demonstrates how to build a production-ready priority-based message processing system using AWS managed services. By combining Amazon MQ priority queuing with DynamoDB real-time streams and App Runner serverless compute, a resilient architecture is created that intelligently handles messages based on business priorities. The implementation of application-level delays with priority bypass ensures critical messages receive immediate attention, and the dual-layer retry mechanism provides maximum reliability. Real-time WebSocket updates keep users informed of processing status, creating a responsive and transparent system. To learn more about the services and patterns used in this solution, explore the following resources:
- AWS documentation and guides:
- Reference architectures and solutions:
- Video tutorials: