From OpenAI to Open LLMs with Messages API on Hugging Face
- Create an Inference Endpoint
- Using Inference Endpoints with OpenAI client libraries
- Integrate with LangChain and LlamaIndex
- Cleaning up
- Conclusion
The Messages API has been introduced to enable OpenAI compatibility with Text Generation Inference (TGI) and Inference Endpoints.
Version 1.4.0 of TGI now includes an API that is compatible with the OpenAI Chat Completion API. This new Messages API facilitates a smooth transition from OpenAI models to open Large Language Models (LLMs). It can be directly utilized with OpenAI’s client libraries or integrated with third-party tools such as LangChain or LlamaIndex.
“The new Messages API, with its OpenAI compatibility, simplifies the process for Ryght’s real-time GenAI orchestration platform to shift LLM use cases from OpenAI to open models. The transition from GPT4 to Mixtral/Llama2 on Inference Endpoints is straightforward, providing a streamlined workflow and enhanced control over AI solutions.” – Johnny Crupi, CTO at Ryght
The Messages API is now accessible within Inference Endpoints, supporting both dedicated and serverless configurations. To assist with implementation, detailed examples are provided for:
- Create an Inference Endpoint
- Using Inference Endpoints with OpenAI client libraries
- Integrate with LangChain and LlamaIndex
Limitations: The Messages API currently lacks support for function calling. It is compatible only with LLMs that have a chat_template defined in their tokenizer configuration, such as Mixtral 8x7B Instruct.
Create an Inference Endpoint
Inference Endpoints provides a secure, production-ready solution for deploying machine learning models from the Hugging Face Hub onto dedicated, managed infrastructure.
This example demonstrates deploying Nous-Hermes-2-Mixtral-8x7B-DPO, a fine-tuned Mixtral model, to Inference Endpoints using Text Generation Inference.
The model can be deployed with a few clicks through the UI, or programmatically using the huggingface_hub Python library. This guide focuses on using the Hub library.
The API call requires specifying the endpoint name, model repository, and the text-generation task. A protected type is used in this example, meaning a valid Hugging Face token is necessary to access the deployed endpoint. Hardware configurations, including vendor, region, accelerator, instance type, and size, also need to be set. Available resource options can be found via this API call, and recommended configurations for certain models are listed here.
Note: A quota upgrade might be required; requests can be sent to [email protected]
from huggingface_hub import create_inference_endpoint
endpoint = create_inference_endpoint(
"nous-hermes-2-mixtral-8x7b-demo",
repository="NousResearch/Nous-Hermes-2-Mixtral-8x7B-DPO",
framework="pytorch",
task="text-generation",
accelerator="gpu",
vendor="aws",
region="us-east-1",
type="protected",
instance_type="nvidia-a100",
instance_size="x2",
custom_image={
"health_route": "/health",
"env": {
"MAX_INPUT_LENGTH": "4096",
"MAX_BATCH_PREFILL_TOKENS": "4096",
"MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS": "32000",
"MAX_BATCH_TOTAL_TOKENS": "1024000",
"MODEL_ID": "/repository",
},
"url": "ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:sha-1734540", # use this build or newer
},
)
endpoint.wait()
print(endpoint.status)
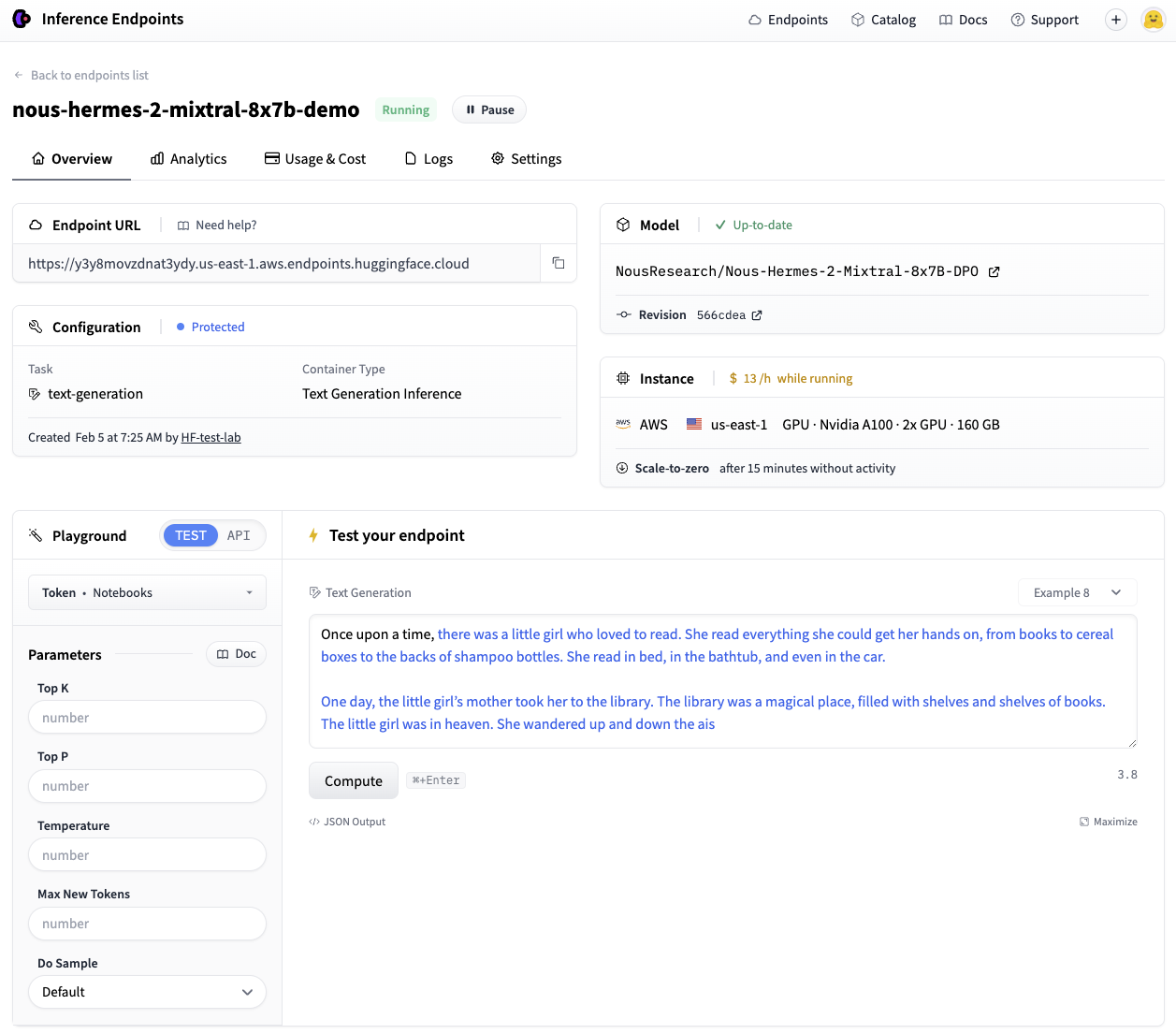
Deployment may take several minutes. The .wait() utility can be used to pause the current thread until the endpoint achieves a “running” status. Once operational, its status can be verified, and it can be tested using the UI Playground:
The endpoint is now operational.
When deploying with huggingface_hub, endpoints are configured to scale to zero after 15 minutes of inactivity by default, helping to optimize costs. The Hub Python Library documentation offers comprehensive details on managing endpoint lifecycles.
Using Inference Endpoints with OpenAI client libraries
TGI’s Messages API enables Inference Endpoints to be directly compatible with the OpenAI Chat Completion API. This allows existing scripts utilizing OpenAI models through their client libraries to seamlessly switch to any open LLM deployed on a TGI endpoint.
This smooth transition provides immediate access to several advantages of open models:
- Complete control and transparency over models and data
- No more worrying about rate limits
- The ability to fully customize systems according to specific needs
Here’s how to achieve this.
With the Python client
The following example demonstrates this transition using the OpenAI Python Library. Users should replace <ENDPOINT_URL> with their endpoint URL (ensuring the v1/ suffix is included) and provide a valid Hugging Face user token in the <HF_API_TOKEN> field. The <ENDPOINT_URL> can be obtained from the Inference Endpoints UI or from the endpoint object’s URL attribute.
The client can then be used conventionally, by passing a list of messages to stream responses from the Inference Endpoint.
from openai import OpenAI
# initialize the client but point it to TGI
client = OpenAI(
base_url="<ENDPOINT_URL>" + "/v1/", # replace with your endpoint url
api_key="<HF_API_TOKEN>", # replace with your token
)
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="tgi",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Why is open-source software important?"},
],
stream=True,
max_tokens=500
)
# iterate and print stream
for message in chat_completion:
print(message.choices[0].delta.content, end="")
The TGI Messages API automatically converts the message list into the model’s required instruction format using its chat template.
Certain OpenAI features, such as function calling, are not currently compatible with TGI. The Messages API supports chat completion parameters including stream, max_tokens, frequency_penalty, logprobs, seed, temperature, and top_p.
With the JavaScript client
The same streaming example is provided below, implemented with the OpenAI Javascript/Typescript Library.
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({
baseURL: "<ENDPOINT_URL>" + "/v1/", // replace with your endpoint url
apiKey: "<HF_API_TOKEN>", // replace with your token
});
async function main() {
const stream = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "tgi",
messages: [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: "Why is open-source software important?" },
],
stream: true,
max_tokens: 500,
});
for await (const chunk of stream) {
process.stdout.write(chunk.choices[0]?.delta?.content || "");
}
}
main();
Integrate with LangChain and LlamaIndex
This section demonstrates how to integrate the newly created endpoint with popular RAG frameworks.
How to use with LangChain
To integrate with LangChain, instantiate ChatOpenAI and provide the <ENDPOINT_URL> and <HF_API_TOKEN> as shown:
from langchain_community.chat_models.openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model_name="tgi",
openai_api_key="<HF_API_TOKEN>",
openai_api_base="<ENDPOINT_URL>" + "/v1/",
)
llm.invoke("Why is open-source software important?")
The existing ChatOpenAI class, typically used with OpenAI models, can be directly leveraged. This enables previous code to function with the endpoint by modifying a single line. The LLM can then be utilized in a basic RAG pipeline to answer questions based on a Hugging Face blog post.
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableParallel
from langchain_community.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
# Load, chunk and index the contents of the blog
loader = WebBaseLoader(
web_paths=("https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents",),
)
docs = loader.load()
# Declare an HF embedding model and vector store
hf_embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="BAAI/bge-large-en-v1.5")
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=512, chunk_overlap=200)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=hf_embeddings)
# Retrieve and generate using the relevant pieces of context
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt")
def format_docs(docs):
return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
rag_chain_from_docs = (
RunnablePassthrough.assign(context=(lambda x: format_docs(x["context"])))
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
rag_chain_with_source = RunnableParallel(
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
).assign(answer=rag_chain_from_docs)
rag_chain_with_source.invoke("According to this article which open-source model is the best for an agent behaviour?")
{
"context": [...],
"question": "According to this article which open-source model is the best for an agent behaviour?",
"answer": " According to the article, Mixtral-8x7B is the best open-source model for agent behavior, as it performs well and even beats GPT-3.5. The authors recommend fine-tuning Mixtral for agents to potentially surpass the next challenger, GPT-4.",
}
How to use with LlamaIndex
A TGI endpoint can also be used with LlamaIndex. This involves using the OpenAILike class and configuring arguments such as is_local, is_function_calling_model, is_chat_model, and context_window. The context_window argument must correspond to the MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS value previously defined for the endpoint.
from llama_index.llms import OpenAILike
# Instantiate an OpenAILike model
llm = OpenAILike(
model="tgi",
api_key="<HF_API_TOKEN>",
api_base="<ENDPOINT_URL>" + "/v1/",
is_chat_model=True,
is_local=False,
is_function_calling_model=False,
context_window=32000,
)
# Then call it
llm.complete("Why is open-source software important?")
The endpoint can then be integrated into a similar RAG pipeline. It is important to note that the MAX_INPUT_LENGTH chosen for the Inference Endpoint directly impacts the number of retrieved chunks (similarity_top_k) the model can process.
from llama_index import (
ServiceContext,
VectorStoreIndex,
)
from llama_index import download_loader
from llama_index.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbedding
from llama_index.query_engine import CitationQueryEngine
SimpleWebPageReader = download_loader("SimpleWebPageReader")
documents = SimpleWebPageReader(html_to_text=True).load_data(
["https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents"]
)
# Load embedding model
embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding(model_name="BAAI/bge-large-en-v1.5")
# Pass LLM to pipeline
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(embed_model=embed_model, llm=llm)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents, service_context=service_context, show_progress=True
)
# Query the index
query_engine = CitationQueryEngine.from_args(
index,
similarity_top_k=2,
)
response = query_engine.query(
"According to this article which open-source model is the best for an agent behaviour?"
)
According to the article, Mixtral-8x7B is the best performing open-source model for an agent behavior [5]. It even beats GPT-3.5 in this task. However, it's worth noting that Mixtral's performance could be further improved with proper fine-tuning for function calling and task planning skills [5].
Cleaning up
Once an endpoint is no longer needed, it can be paused or deleted. This action can be performed through the UI or programmatically as demonstrated below.
# pause our running endpoint
endpoint.pause()
# optionally delete
endpoint.delete()
Conclusion
The Messages API within Text Generation Inference offers a streamlined migration from OpenAI models to open LLMs. This capability is expected to enable a wide range of new applications powered by open LLMs on TGI.
A runnable version of the code presented in this post is available in this notebook.
More Articles from the Blog